|
|
| (47 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | + | <!-- |
| | {{Zoltan}} | | {{Zoltan}} |
| − |
| |
| | {{DavidBeraha}} | | {{DavidBeraha}} |
| | | | |
| − | {{Tidy1}} | + | {{Comment}}, |
| | | | |
| − | {{Clustering stage}}, | + | {{Consolidation stage}}, |
| | | | |
| − | {{Content}}, | + | {{Priority}}, |
| | + | --> |
| | | | |
| − | {{Links}}
| |
| | ==Definition== | | ==Definition== |
| − | {{PAGENAME}} is {{ {{PAGENAME}} }}
| + | {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} |
| | | | |
| − | == Summary== | + | == Description == |
| | + | A Self-Assessment is a valuable tool to help determine the current intellectual capital (IC) needs, including human capital (competencies in people), structural capital (policies, formal and informal processes, data and information owned by the organisation) and relation capital (relationships the organisation has with other organisations and individuals) in order to assist in identifying areas for future improvement, thus providing the basis for the formulation of KM strategies and policies. IAEA has developed a practical self-assessment tool adaptable to the type of the organization containing a questionnaire and a spreadsheet with graphical presentation of the results. |
| | | | |
| − | == Description == | + | === Methodology === |
| | A Self-Assessment is a valuable tool to help determine the current [[Knowledge management|KM]] capability in an organization and to | | A Self-Assessment is a valuable tool to help determine the current [[Knowledge management|KM]] capability in an organization and to |
| − | assist in identifying KM areas for future improvement, thus providing the basis for the formulation of KM strategies and policies. It may be initially performed when exploring the possibility of introducing the KM concepts, methodologies and tools, or as an ongoing continous effort to verify the improvements of the KM system and the KM maturity level of the organization. | + | assist in identifying KM areas for future improvement, thus providing the basis for the formulation of [[NKM strategy | NKM strategies]] and [[NKM policy | policies]]. It may be initially performed when exploring the possibility of introducing the KM concepts, methodologies and tools, or as an ongoing continous effort to verify the improvements of the KM system and the KM maturity level of the organization. |
| | | | |
| − | The self-assessment is performed in relation to the key elements in KM. These key elements may vary according to the type of the organization. Indeed, a preliminary stage previous to conducting the self-assessment may be necessary in order to adapt the self-assessment questions to the specific situation and needs of the organization. For this purpose, an organization planning to conduct a self-assessment should consider requesting help from IAEA, e.g. in form of an assist mission. The process for required to initiate this can be found in Ref. [1]. | + | The IAEA has produced a self-assessment questionnaire which is adaptable to different organization types, and provides an Excel-spreadsheet to conduct the self-assessment in groups and to evaluate the results of the assessment in a graphical form. |
| | | | |
| − | The self-assessment may be performed on different organizational levels. When considering the implementation of a KM system in the organization, the targeted audience will primarily consist of high and upper level management. Self-assessments may also be conducted on unit levels, particularly for recurrent self-assessments with the aim of improving KM performance. | + | The self-assessment is performed in relation to the key elements in KM. These key elements may vary according to the type of the organization. Indeed, a preliminary stage previous to conducting the self-assessment may be necessary in order to adapt the self-assessment questions to the specific situation and needs of the organization. For this purpose, an organization planning to conduct a self-assessment should consider requesting help from IAEA, e.g. in form of an assist mission. The process for required to initiate this can be found in Ref. [1]. |
| | | | |
| − | The self-assessment questionnaire is best used in a group or workshop environment and can be completed by collecting responses from a number of people who are knowledgeable with regards to the organization’s activities and future goals. | + | The self-assessment may be performed on different organizational levels. When considering the implementation of a KM system in the organization, the targeted audience will primarily consist of high and upper level management. Self-assessments may also be conducted on unit levels, particularly for recurrent self-assessments with the aim of improving KM performance. The self-assessment questionnaire is best used in a group or workshop environment and can be completed by collecting responses from a number of people who are knowledgeable with regards to the organization’s activities and future goals. |
| | | | |
| − | === Example ===
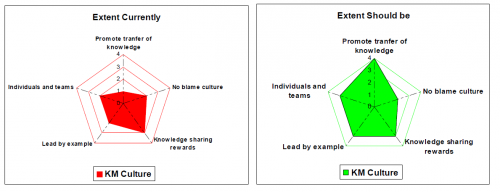
| + | [[File:1586_appendix_fig08.png|500px|thumbnail|right| Fig. 1 Example output]] |
| − | Examples of the self-assessment questionnaire have been published [1], [2] or will be published in the organization-specific publications. The example from [1] is given here:
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | The self-assessment methodology described here is intended to provide participants, including senior management, with a tool to help identify strengths and development areas in the organization’s overall KM strategy.
| + | As a result of the self-assessment, the radar graphs shows the distance between the target and the actual value for each of the key elements (see the example output in Fig. 1, indicating the aereas where the KM level is sufficient (or even overachieved), and aereas where improvement is needed. This will guide the implementation of the KM system resp. of new or additional features. |
| − | Individual criteria have been identified that are considered as key elements towards an effective approach to KM. These criteria have been grouped into seven organizational or functional categories, to facilitate the self-assessment, via:
| + | |
| − | Policy/Strategy
| + | |
| − | Human Resource (HR) Planning and HR Processes
| + | |
| − | Training and Human Performance Improvement
| + | |
| − | Methods, Procedures & Documentation Processes for Improving KM
| + | |
| − | Technical (IT) Solutions
| + | |
| − | Approaches to Capture/Use Tacit Knowledge
| + | |
| − | KM culture/Workforce Culture Supporting KM
| + | |
| − | Metrics for the overall self-assessment and for each individual category have been developed as shown below:
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | KM Self-Assessment Metrics Scoring
| + | === Self-assessment as a basis for developing a KM strategy === |
| − | Rating Extent Currently Extent Should Be
| + | A self-assessment, possibly aided by external experts from IAEA or other institutions, usually provides a good starting point for developing the KM strategy. The self assessment shows the difference between the current state of KM maturity and the desired level, to which KM should be developed. Following the steps outlined in KM strategy, a suitable approach (either top-down or bottom-up) should be chosen, followed by the specification of objectives. In KM strategy, the items to be considered in developing a strategy are described in more detail, as well as the outline of a proposed structure for the strategy document. The KM strategy, together with policies developed within it, provides a sound foundation for the implementation of knowledge management. |
| − | 0 Not utilized at all Not utilized at all
| + | |
| − | 1 To a little extent To a little extent
| + | |
| − | 2 To some extent To some extent
| + | |
| − | 3 To a great extent To a great extent
| + | |
| − | 4 To a very great extent To a very great extent
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | A self assessment questionnaire has been developed based on the above seven categories. A Microsoft Excel based tool is also available that is used to facilitate the self assessment process. The tool uses radar/spider diagrams for each of the seven functional categories and at an executive summary level to give management a graphical depiction of current KM strengths and future development areas. An example of the output is given below:
| + | ==Examples== |
| | + | Examples of the self-assessment questionnaire have been published in [1], [2] or will be published in the publications treating organization-specific KM. The example from [1] is shown here: [[Knowledge management assessment tool| KM Assessment Tool]] |
| | | | |
| | + | == References == |
| | + | [1] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions For Nuclear Organizations, IAEA- TECDOC-1586, IAEA, Vienna (2008) |
| | | | |
| | + | [2] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Knowledge Management for Nuclear Research and Development Organizations, IAEA- TECDOC-1675, IAEA, Vienna (2012) |
| | | | |
| − | Example output
| + | ==Related articles== |
| | + | [[NKM policy]] |
| | | | |
| − | Self-assessment can be used independently by a nuclear operating organization for an internal review, as a prerequisite for a KM assist mission or during a KM assist mission. These criteria are not so much intended to provide a “report card” as they are to assist managers in identifying strengths to build upon and areas for improvement to be addressed in the knowledge management area.
| + | [[Maturity model]] |
| | | | |
| − | [edit]15.1 Policy/Strategy | + | [[Knowledge management maturity assessment]] |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | Written policies/strategies
| + | |
| − | Communication strategy
| + | |
| − | Identification of KM responsibilities
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [1–7].
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the organization have a written policy for
| + | |
| − | implementing its strategy in KM area?
| + | |
| − | 2 Is a KM policy integrated into the management
| + | |
| − | system?
| + | |
| − | 3 Is the KM policy communicated to all staff in the
| + | |
| − | organization?
| + | |
| − | 4 Are those responsible for managing the formulation
| + | |
| − | and implementation of the organization KM strategy clearly identified?
| + | |
| − | 5 Does the organization’s strategic focus support
| + | |
| − | continuous learning to improve individual and organizational performance?
| + | |
| − | 6 Is the organization’s KM policy aligned with
| + | |
| − | continued emphasis on a strong safety culture?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output (in form of a radar/spider diagram) for the category 1 is given below
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [edit]15.2 Human resource (HR) planning & HR processes
| + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | Workforce planning
| + | |
| − | Succession planning
| + | |
| − | Risk assessment for critical knowledge loss
| + | |
| − | Employee development plans for KM
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [3, 4, 6, 8–12]
| + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the organization have a written policy for
| + | |
| − | implementing its strategy in KM area?
| + | |
| − | 2 Is a KM policy integrated into the management
| + | |
| − | system?
| + | |
| − | 3 Is the KM policy communicated to all staff in the
| + | |
| − | organization?
| + | |
| − | 4 Are those responsible for managing the formulation
| + | |
| − | and implementation of the organization KM strategy clearly identified?
| + | |
| − | 5 Does the organization’s strategic focus support
| + | |
| − | continuous learning to improve individual and organizational performance?
| + | |
| − | 6 Is the organization’s KM policy aligned with
| + | |
| − | continued emphasis on a strong safety culture?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the organization implement a comprehensive
| + | |
| − | methodology to ensure that HR needs both current and future are met (work force planning)?
| + | |
| − | 2 Is there an effective succession planning
| + | |
| − | programme in place?
| + | |
| − | 3 Are risk assessments carried out to identify
| + | |
| − | potential loss of critical knowledge and skills?
| + | |
| − | 4 Are exit interviews carried out to capture critical
| + | |
| − | knowledge and experience when people leave the organization?
| + | |
| − | 5 Does a programme exist to develop new leadership
| + | |
| − | /technical talent in a timely manner?
| + | |
| − | 6 Does the organization utilise job profiles or
| + | |
| − | equivalent to assess and monitor its skills/competency needs?
| + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 2 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [edit]15.3 Training and human performance improvement
| + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | Coaching and mentoring
| + | |
| − | SAT
| + | |
| − | Simulator use
| + | |
| − | CBT (e-learning)
| + | |
| − | Refresher training
| + | |
| − | Human Performance Improvement
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [4, 6, 9, 10, 13–19]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the organization incorporate formal
| + | |
| − | Systematic Approach to Training (SAT) principles into its training programmes?
| + | |
| − | 2 Does the formal SAT programme address capture
| + | |
| − | and dissemination of knowledge?
| + | |
| − | 3 Does the training programme utilise appropriate
| + | |
| − | tools such as simulators, Computer Based Training (CBT), multi-media simulations, etc. to capture/transfer critical knowledge?
| + | |
| − | 4 Is competence evaluated on a regular basis?
| + | |
| − | 5 Is regular refresher training carried out to maintain
| + | |
| − | and enhance competence?
| + | |
| − | 6 Does the organization have a formal human
| + | |
| − | performance improvement programme to maintain and enhance competence?
| + | |
| − | 7 Are coaching and mentoring approaches used to
| + | |
| − | support knowledge sharing?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 3 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [edit]15.4 Methods, procedures & documentation processes for improving KM
| + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | Learning from Operating Experience
| + | |
| − | Work control methods
| + | |
| − | Error prevention
| + | |
| − | Document control/Configuration
| + | |
| − | Corrective action programme
| + | |
| − | Benchmarking
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [3, 4, 18–27]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Are KM methods incorporated into
| + | |
| − | procedures and processes rather than being separate add-on tasks?
| + | |
| − | 2 Does the organization have a
| + | |
| − | comprehensive methodology that addresses learning from experience?
| + | |
| − | 3 Are self assessments regularly used to
| + | |
| − | enhance organizational knowledge?
| + | |
| − | 4 Is external benchmarking regularly used
| + | |
| − | to enhance organizational knowledge by adopting good industry practices?
| + | |
| − | 5 Is the feedback (internal and external)
| + | |
| − | from operational experience (lessons learned) used by the organization for corrective action planning to achieve improvements?
| + | |
| − | 6 Is the composition of work teams (such as
| + | |
| − | individual expertise/experience) considered in order to enhance knowledge transfer?
| + | |
| − | 7 Are all work activities documented in
| + | |
| − | such a way that knowledge can be effectively retrieved, shared and utilized?
| + | |
| − | 8 Are procedures, drawings, lesson plans
| + | |
| − | and related documentation updated promptly in a systematic way to address technical and organizational changes?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 4 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | Knowledge data bases | + | |
| − | Content/document management systems
| + | |
| − | Search engines
| + | |
| − | Portals/Intranet
| + | |
| − | Wikis/blogs
| + | |
| − | Skill/competency databases
| + | |
| − | Expert yellow pages
| + | |
| − | Enterprise Resource Planning (EPR)
| + | |
| − | Other IT supporting systems
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [3–5, 21, 28, 29]
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Are IT and KM strategies aligned?
| + | |
| − | 2 Is the organization utilising an integrated approach
| + | |
| − | in managing its information?
| + | |
| − | 3 Does the organization utilise appropriate IT support
| + | |
| − | systems and tools such as:
| + | |
| − | 3.1
| + | |
| − | Content/document management
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.2
| + | |
| − | Concept mapping
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.3
| + | |
| − | Knowledge databases
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.4
| + | |
| − | Simulation tools
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.5
| + | |
| − | Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.6
| + | |
| − | Portals/Intranets
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.7
| + | |
| − | Knowledge search engines
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.8
| + | |
| − | Expert yellow pages
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.9
| + | |
| − | Expert systems
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3.10
| + | |
| − | Wiki’s/blogs
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 5 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [edit]15.5 Approaches to capture/use tacit knowledge
| + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | • Taxonomy development • Process for critical knowledge ID • Processes for knowledge elicitation/harvesting • Concept mapping • COPs • Coaching & mentoring
| + | |
| − | For background information see References [1, 4, 5, 8].
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the organization utilise methods to identify
| + | |
| − | people who have critical knowledge?
| + | |
| − | 2 Does the organization adopt effective techniques to
| + | |
| − | capture critical knowledge such as:
| + | |
| − | 2.1
| + | |
| − | Elicitation interviews
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.2
| + | |
| − | Video capture
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.3
| + | |
| − | On the Job Training (OJT) dialogue
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.4
| + | |
| − | Mentoring/coaching
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.5
| + | |
| − | Communities of Practice (COP)
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.6
| + | |
| − | Explicit capture (narrative documentation)
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.7
| + | |
| − | Card sorting (manual concept map)
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.8
| + | |
| − | Concept mapping
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.9
| + | |
| − | Process mapping
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.10
| + | |
| − | Story telling
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 2.11
| + | |
| − | Others
| + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | 3 Is information and data retained and presented in
| + | |
| − | an effective way to facilitate search and retrieval?
| + | |
| − | 4 Does the organization have processes for the
| + | |
| − | effective transfer and utilisation of captured knowledge?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 6 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | [edit]15.6 KM culture/workforce culture supporting KM
| + | |
| − | This topic covers the following aspects:
| + | |
| − | No blame environment
| + | |
| − | Sharing knowledge
| + | |
| − | Leadership/commitment
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | For background information see References [1, 3, 4, 19].
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | No.
| + | |
| − | Assessment Criteria/Questions Extent currently utilized Extent should be utilized
| + | |
| − | Comments
| + | |
| − | 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4
| + | |
| − | 1 Does the culture of the organization promote the
| + | |
| − | sharing and transfer of knowledge, particularly tacit knowledge, amongst personnel?
| + | |
| − | 2 Does the organization have an open, no blame
| + | |
| − | approach to reporting incidents/events and sharing from lessons learned?
| + | |
| − | 3 Is sharing of knowledge in the
| + | |
| − | organization recognised and rewarded?
| + | |
| − | 4 Do managers lead by example performing
| + | |
| − | practical, visible leadership supporting the knowledge management strategy?
| + | |
| − | 5 Do managers encourage trust, cooperation and
| + | |
| − | collaboration between individuals and teams?
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | An example of the output for the category 7 is given below:
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | Example output
| + | |
| − | [edit]16 Appendix II - End of mission report contents
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | The following content is required for each of End of Mission Report. The report will have six main sections as detailed below with Appendices as required for detailed information captured during the mission.
| + | |
| − | Examples of previous mission reports are available from the IAEA on request but are subject to confidentiality restrictions.
| + | |
| − | ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION - This section contains project information related to the mission and comprises:
| + | |
| − | project number
| + | |
| − | project title
| + | |
| − | task title
| + | |
| − | list of participating experts
| + | |
| − | dates of the assignment
| + | |
| − | Counterpart information, i.e. names and location
| + | |
| − | duty station location
| + | |
| − | IAEA programme reference – i.e. Sub Programme C.3. Nuclear Knowledge Management
| + | |
| − | TERMS OF REFERENCE - This section describes the objectives of the mission, the mission scope and duties. Three separate sub-sections apply:
| + | |
| − | objectives of mission – This is a paragraph describing the mission objectives as agreed with the Counterpart prior to commencement.
| + | |
| − | mission scope – This details the KM areas addressed during the mission.
| + | |
| − | mission duties – This is a paragraph describing the form of the mission, i.e. how the mission was conducted (e.g. preparation & delivery of presentations, meetings with senior management etc.)
| + | |
| − | BACKGROUND -This section provides background to the visit in the context of knowledge management and the issues the nuclear industry is facing worldwide. If there are specific issues within the host country, organization or plant then these should also be specified here. Typically three or four paragraphs are provided here.
| + | |
| − | WORK PROGRAMME - This section outlines the programme of work undertaken during the visit with details of dates, times, locations and responsibilities. It can consist of the agreed agenda as prepared prior to the visit with any modifications as appropriate.
| + | |
| − | RECOMMENDATIONS TO THE IAEA - This section contains recommendations to the IAEA that are received from the Counterpart, Experts or other parties involved with the mission. The recommendations to the IAEA may consist of:
| + | |
| − | Strategic IAEA initiatives that should be undertaken to support generic KM issues
| + | |
| − | Suggestions for further IAEA work at the Counterpart’s location.
| + | |
| − | Suggestions involving government action or coordinated activity in the Counterpart’s country.
| + | |
| − | Other recommendations that are relevant to KM that can be executed directly or facilitated by the IAEA.
| + | |
| − | RECOMMENDATIONS TO THE COUNTERPART - This section contains the combined recommendations from the IAEA team. The recommendations are varied in nature and should be grouped in order according to the locations or organizations visited. The recommendations should aim to identify good practice areas as well as areas that need to be developed. Typical recommendations will cover one or more of the following issues:
| + | |
| − | Observations of good practice.
| + | |
| − | Strategic recommendations that may involve central government, multiple organizations or political factors.
| + | |
| − | General recommendations, applicable to the Counterpart’s organization, that relate to KM improvement.
| + | |
| − | Specific recommendations that could be applied to the Counterpart’s organization that relate to KM improvement. This would typically be at the technology, process or HR level and may involve good practice techniques used in similar organizations.
| + | |
| − | Wherever possible, the IAEA team will endeavour to provide pragmatic advice that can be translated into an action plan by the Counterpart at the end of the mission.
| + | |
| − | LIST OF APPENDIXES
| + | |
| − | Appendices are included as required and may contain information such as presentation summaries, lists of participants, self assessment output, contact details, and other information that is requested or provides value to the Counterpart
| + | |
| − | [edit]17 Appendix III - KM assist mission critique
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | KM Assist mission critique - page 1.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | KM Assist mission critique - page 3.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | KM Assist mission critique - page 2.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − |
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | KM Assist mission critique - page 4.
| + | |
| − | | + | |
| − | == References ==
| + | |
| − | ==Related articles==
| + | |
| − | [[KM assist mission]]
| + | |
| | | | |
| − | [[category:Tools]] | + | [[Category:Assessment]] |
The process of conducting an assessment of knowledge management maturity within the own organization and by its own staff
A Self-Assessment is a valuable tool to help determine the current intellectual capital (IC) needs, including human capital (competencies in people), structural capital (policies, formal and informal processes, data and information owned by the organisation) and relation capital (relationships the organisation has with other organisations and individuals) in order to assist in identifying areas for future improvement, thus providing the basis for the formulation of KM strategies and policies. IAEA has developed a practical self-assessment tool adaptable to the type of the organization containing a questionnaire and a spreadsheet with graphical presentation of the results.
The IAEA has produced a self-assessment questionnaire which is adaptable to different organization types, and provides an Excel-spreadsheet to conduct the self-assessment in groups and to evaluate the results of the assessment in a graphical form.
The self-assessment is performed in relation to the key elements in KM. These key elements may vary according to the type of the organization. Indeed, a preliminary stage previous to conducting the self-assessment may be necessary in order to adapt the self-assessment questions to the specific situation and needs of the organization. For this purpose, an organization planning to conduct a self-assessment should consider requesting help from IAEA, e.g. in form of an assist mission. The process for required to initiate this can be found in Ref. [1].
The self-assessment may be performed on different organizational levels. When considering the implementation of a KM system in the organization, the targeted audience will primarily consist of high and upper level management. Self-assessments may also be conducted on unit levels, particularly for recurrent self-assessments with the aim of improving KM performance. The self-assessment questionnaire is best used in a group or workshop environment and can be completed by collecting responses from a number of people who are knowledgeable with regards to the organization’s activities and future goals.
As a result of the self-assessment, the radar graphs shows the distance between the target and the actual value for each of the key elements (see the example output in Fig. 1, indicating the aereas where the KM level is sufficient (or even overachieved), and aereas where improvement is needed. This will guide the implementation of the KM system resp. of new or additional features.
A self-assessment, possibly aided by external experts from IAEA or other institutions, usually provides a good starting point for developing the KM strategy. The self assessment shows the difference between the current state of KM maturity and the desired level, to which KM should be developed. Following the steps outlined in KM strategy, a suitable approach (either top-down or bottom-up) should be chosen, followed by the specification of objectives. In KM strategy, the items to be considered in developing a strategy are described in more detail, as well as the outline of a proposed structure for the strategy document. The KM strategy, together with policies developed within it, provides a sound foundation for the implementation of knowledge management.
Examples of the self-assessment questionnaire have been published in [1], [2] or will be published in the publications treating organization-specific KM. The example from [1] is shown here: KM Assessment Tool
[1] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions For Nuclear Organizations, IAEA- TECDOC-1586, IAEA, Vienna (2008)
[2] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Knowledge Management for Nuclear Research and Development Organizations, IAEA- TECDOC-1675, IAEA, Vienna (2012)