Knowledge loss risk assessment in NPP's
Contents
Definition
One sentence definition. A template can be used for definition.
Summary
One paragaph summary which summarises the main ideas of the article.
Description
The following processes and tools can be used by nuclear power plants to identify and mitigate knowledge loss threats. Management can adapt or modify these processes and tools to meet the specific needs of their organization.
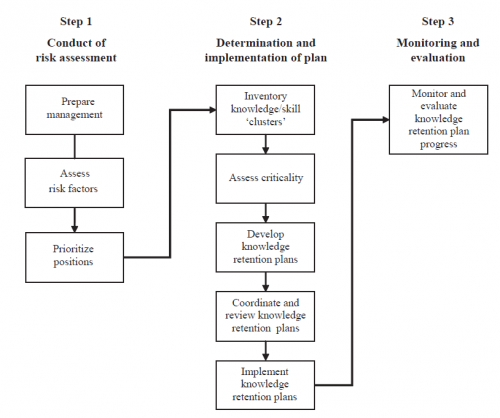
Attrition related knowledge loss threats can be identified, prioritized and addressed using the following process to determine a total risk factor for each employee in the organization. This total risk factor is based on a projected attrition date, which could be retirement, transfer, or other attrition (attrition risk factor), and criticality of knowledge and skill (position risk factor). This three step process has been succesfully implemented by the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) in the USA. Figure 1 is a flow diagram of the critical knowledge retention process. Knowledge retention roles and responsibilities are outlined in Annex I.
The three step process
Step 1
Conduct of a knowledge loss risk assessment The knowledge loss risk assessment is designed to identify positions/ individuals where the potential for knowledge loss is greatest and most imminent.
The attrition risk factor is based on the expected retirement or other attrition date. The date can be provided by the employee or calculated according to age and tenure data. Table 1 lists the criteria used to assign an attrition risk factor.
The position risk factor is initially assigned by the department level manager using criteria listed in Table 2. The position risk factor criteria are based on the unique/critical knowledge and skills possessed by the employee and an estimate of the difficulty or level of effort required to refill the position. In assigning the factor the manager should consider each employee’s responsibilities and background, formal and informal roles, collateral duties, recurrent assignments (e.g. outage related duties, problem solving or trouble shooting assignments) and other factors suggesting that the employee may have unique/ critical knowledge and skills. Department managers may want to consult other work group members, key plant customers, or interested parties when determining ratings.
The total risk factor of an employee is determined on the basis of the guidelines provided in Table 3. The total risk factor provides an overall assessment of attrition related risk for knowledge loss. The total risk factor is computed by multiplying the attrition risk factor by the position risk factor (see Table 4).
Each nuclear power plant management team should collectively review the results of the risk assessment. Experience has shown that a critical review of
Employee self-assessment–knowledge retention process
Risk management of institutional knowledge loss
Source: Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Industry Organizations
References
[1]