Knowledge
Contents
Definition
Knowledge is A mix of experiences, values, contextual information and expert insight for acquiring, understanding and interpreting information. Together with attitudes and skills, it forms a capacity for effective actions.
Summary
Knowledge is a mix of experiences, values, contextual information and expert insight for acquiring, understanding and interpreting information. Together with attitudes and skills, it forms a capacity for effective action. It is part of the data-information-knowledge-wisdom value-added chain. Knowledge has several dimensions: types (explicit, implicit, tacit), holders (individual, group, organizational, sector), levels (know-why, know-what, know-how). Knowledge is an asset, it is not static and continually progresses through a lifecycle.
Description
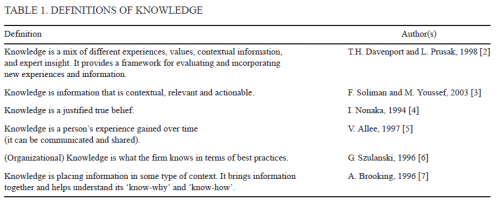
Since the time of the earliest philosophers men and women have attempted to both understand and define the concept of knowledge, however, no single definition of knowledge exists that has been generally agreed upon. Table 1 shows some of the definitions:
Many knowledge models exist. Two of the more practical models are described below
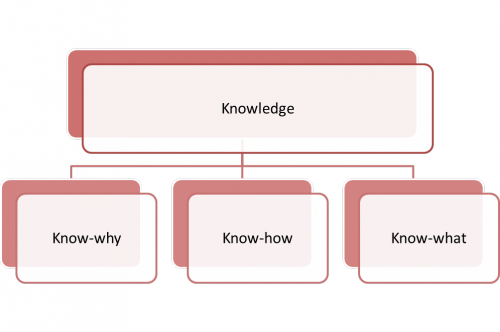
Know-why,know-how,know-what knowledge model
Know-how usually refers to knowledge on how to accomplish something and implies practical knowledge or skills giving the holder of such knowledge the ability to execute tasks of a practical nature. Know-what often refers to the facts about a certain subject. Know-why refers to the knowledge about theoretical knowledge and an understanding of causal relationships, interactive effects and uncertainty levels associated with a given situations which can be used to find new solutions and solve problems.
A simple example to illustrate this is the need for different types of knowledge when jumping into deep water. Know-how is the ability to swim, know-what is knowing what arm and leg actions are required as they may be presented in a written instruction manual on swimming. Know-why may include an understanding of Archimede's principle and Newton's third law.
This model can be extended to include other aspects of knowledge. As well as know-how, know-why, know-what, we can add know-who, know-when, know-where. This is a useful model for knowledge retention and transfer leading to the employment of practical tools for eliciting and capturing knowledge. For example a Personal network map is one example of a tool used for transfering know-who, know-when and know-where.
Domains knowledge model
definitions
For our purpose, the following definition will be used:
Know-how is a term for practical knowledge on how to accomplish something, as opposed to “know-what” (facts), “know-why” (science) Knowledge is a mix of experiences, values, contextual information and expert insight for acquiring, understanding and interpreting information. Together with attitudes and skills, it forms a capacity for effective action.
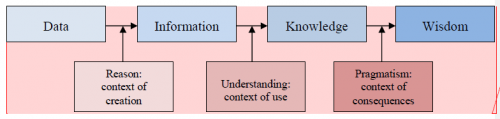
It is important to recognize the distinction between knowledge, information and data. Raw data become information in the context of creation, information becomes knowledge in the context of use, meaning that a human agent (the recipient) with the appropriate background is required (who might act based on this knowledge). Knowledge may eventually lead to wisdom. Fig. 1 shows these relationships.
Knowledge is considered an asset to be managed, it could be an input, it may be embedded in work methods (i.e. part of a process) or it can be a product (i.e. an output). Knowledge may often be time dependent or contextual, and must be maintained and renewed.
Knowledge is not static, it goes through different stages of a lifecycle (i.e. creating, using, sharing, preserving)
In the concept of knowledge, different dimensions are usually considered, e.g. types of knowledge, knowledge holders, knowledge levels (know-why, know-what, know-how etc.)
Explicit,implicit,tacit knowledge model
Explicit, implicit and tacit or the the "Iceberg model of knowledge", is a popular representation of the relationship between explicit and tacit knowledge. Implicit knowledge is that knowledge which could be made explicit if sufficient time and resources were committed to it's conversion. As only part of the explicit knowledge is codified the undocumented knowledge represents an opportunity for knowledge capture
Knowledge holders
Knowledge exists in different forms and at different levels: individual (link), group, organization, sector (e.g. Nuclear knowledge). Although it originates in the minds of individuals, in organizations it often becomes embedded not only in documents or repositories but also in organizational routines, processes, practices, and norms.
Knowledge levels
In practice, a categorization of knowledge by levels is insightful. Those levels are often referred to as know-how, know-why, know-what, know-who, know-when, know-where, the most important ones being know-what (knowledge of facts), know-how (skills), and know-why (theoretical understanding). Know-what is the factual knowledge of all relevant information needed to understand increasingly complex concepts and patterns, and to take appropriate, normed action. Know-how relates to skills allowing to carry out specific tasks. It permits people to determine which treatment is best in given situations, and deciding on different courses of actions. It may be codified in procedures. Know-why as the hightest knowledge level gives the individual a deep understanding of causal relationships, interactive effects and uncertainty levels associated with a given situations, leading to new solutions or non-norm actions.
A learning organization should provide educational and training means for its staff to obtain the necessary knowledge levels in order to accomplish the tasks and activities as stated in the job description.
References
[1] KURONEN, BIT Research Center, Helsinki University of Technology, “What is tacit knowledge in NPP maintenance and what are the prerequisites for sharing it?”, CSNI International Workshop, Ottawa, Canada, 3-5 October 2005.
[2] DAVENPORT, T.H., PRUSAK, L., Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know, Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA (2000).
[3] INTERNATIONAL COUNCIL ON ARCHIVES, Radioactive Waste Information: Meeting Our Obligations to Future Generations with Regard to Safety of Waste Disposal Facilities, ICA Study 18, ICA, Paris (2006).
[4] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist missions for Nuclear Organizations, IAEA-TECDOC-1586, IAEA, Vienna (2008).
[5] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Knowledge Management for Nuclear Industry Operating Organizations, IAEA-TECDOC-1510, IAEA, Vienna (2006).