Explicit knowledge
Template:Monica Template:Andrey Template:Anatoly
 , Template:Foundation,
, Template:Foundation,
Contents
Definition
Explicit knowledge is knowledge Template:Explicit knowledge 4
Summary
One paragraph summary which summarises the main ideas of the article.
Description
Explicit knowledge is knowledge Template:Explicit knowledge 4 This knowledge can be readily transferred to others.
Forms of explicit knowledge
The most common forms of codified explicit knowledge are documents, drawings, calculations, icons, designs, multimedia, databases, knowledge representation (i.e. taxonomies, knowledge maps) documented procedures and manuals.
Non-codified explicit knowledge (i.e., knowledge that is conscious to the knowledge bearer) is for example existing non-documented procedures in an organization
Description
Explicit knowledge is that which can be contained and conveyed in documents, drawings, calculations, designs, databases, procedures and manuals. This type of knowledge is also referred to as information. Explicit knowledge can be recalled and articulated by the bearer, and subsequently recorded (for example, RWM documentation and databases).
Source: Knowledge management for radioactive waste management organisations
Description
Explicit knowledge is contained and conveyed in documents, drawings, calculations, designs, databases, procedures and manuals. Explicit knowledge is knowledge that has already been codified (i.e. written down) or declared.
Source: Comparative Analysis of Methods and Tools for Nuclear Knowledge Preservation
Description
Explicit knowledge is considered to be all the knowledge that can be easily articulated and expressed in writing. This mode of knowledge is contained in documents, drawings, calculations, databases, procedures and manual. The quality assurance system (QAS) should provide for the management of this kind of knowledge.
Source: National approaches and strategies for Nuclear Knowledge Management
Description
Explicit knowledge is contained in documents, drawings, calculations, designs, databases, procedures and manuals. Explicit knowledge implies declared knowledge (i.e., knowledge that is conscious to the knowledge bearer). Explicit knowledge is why it is not a problem for the employee to tell about rules and obviously learned facts. Very often this knowledge is already written down in books. Examples that contain explicit knowledge include NPP documentation and databases such as a website, an operational manual, records or a report of research findings.
Source: Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations
Description
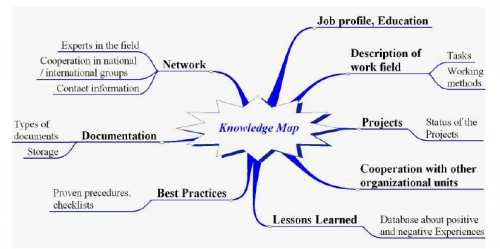
Explicit knowledge implies declared knowledge (i.e. knowledge that is conscious to the knowledge bearer). Explicit knowledge is why it is not a problem for the employee to tell about rules and obviously learned facts. Very often this knowledge is already written down in books. The most important aspects of knowledge can be illustrated by using a knowledge map. Such a tool is helpful in the transfer of knowledge from departing employees to their successors (see Fig. 4).
Source: Knowledge Management for Nuclear Industry Operating Organizations
References
Related articles
Explicit knowledge preservation at the EC Joint Research Centre, Petten