Business process
Contents
Definition
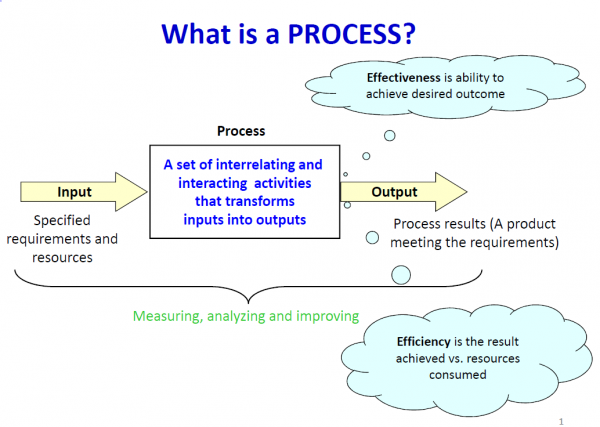
Process is a set of interrelated or interacting activities that transforms inputs into outputs.
Source: IAEA Safety Glossary 2007 Edition
Business process is A managed process that produces business related outcomes
Summary
One paragraph.
Description
What is a process?
In other words a process is a structured and monitored set of activities designed to produce a specified output for a particular customer: both internal and external.
The processes of the management system that are needed to achieve the goals, provide the means to meet all requirements and deliver the products/services of the organization shall be identified, and their development shall be planned, implemented, assessed and continually improved.
All processes should be aligned with the objectives, scope and complexity of the organization, and should be designed to add value to the organization.
Some organizations have found it beneficial to group their processes as core processes, management processes and supporting processes.
The sequence and interactions of the management system processes shall be determined and processes shall be documented to the appropriate extent. To document processes different methods could be used, such as graphical representations, written instructions, checklists, flow charts, methods using visual media and electronic methods.
Complex processes could be devided into sub-processes and further into activities and tasks. To visualize/structure the processes and to reflect all interrelations among the sub-processes (activities or tasks) a process map could be developed that is usually called process model.
Each process has its life cycle, that includes the following stages:
– Process Definition and Design
– Process Implementation
– Process Monitoring and Measurement
– Process Improvement or reengineering
Process Definition and Design
Process Definition and Design includes setting process goals, defining process title, assigning process owner and process structuring to determine logical and streamlined path so that the goals may be effectively and efficiently achieved.
During this stage process title and its customers and other interested parties should be defined. When designing a Business process it is advisable to define all inputs, outputs, owner and participants. The processes flow in sequence and interaction should be determined as well.
Inputs to the process, include requirements, needs and expectations of interested parties ,outputs of other processes, information, etc. to define the intended output and sproces goals and objectives . Process outputs are results/products that can be measured/considered/provided, including its quality characteristics.
Individual roles, responsibilities and authority for ensuring the implementation, maintenance and improvement of the process and its interactions should be assigned. An individual that is managing the process and responsible for the process outcome and effectiveness is usually referred to as the "process owner". The process owner is, as a rule, a post holder that has appropriate knowledge and all the information regarding the process flow and details. To manage complex process and process interactions, in some organizations additionally a "process sponsor" could be assigned or a "process management team" established to provide support to the process owner.
Other process participants are individuals that performe/fullfil specific activities, tasks or functions within the process and ensuring its implementation.
When designing the process the sequence and interaction of the activities within the process, the monitoring and measuring criteria for process control and process performance, the resources needed for the effective operation of the process and how the process shall be documented should be determined.
Process Implementation
Process Implementation involves ensuring process workflow and resourcing process so that each activity is supported with the needed staff, equipment, time, and budget.
The processes and its sub-processes and activities should be implemented as planned. Process management activities include, but are not limited to:
- Leadership and communication,
- Training and awareness,
- Change management,
- Management involvement,
- Applicable review activities.
To maintain satisfactory control of the process the monitoring and measurements should be performed as planned so that it ensures proactive process feedback loop.
Process Monitoring and Measurement
Process Monitoring and Measurement ensures tracking process performance against established goals and performance indicators, giving feedback and identifying deficiencies.
Process effectiveness and efficiency can be assessed through internal or external review processes.
Process Improvement or Reengineering
Process Improvement or Reengineering involves correcting deficiencies and improving performance, resetting goals and redesigning the process when required.
=Test paragraph
Process owner is Template:Process owner.
References
[1] IAEA safety requirements GS-R-3 “Management System for facilities and activities” (2006);
[2] IAEA Safety Guide GS-G-3.1 “Application of management system for facilities and activities” (2006);
[3] IAEA Safety Guide GS-G-3.5 “The management system for nuclear installations” (2009);
[4] IAEA Safety Glossary 2007 Edition;
[5] ISO 9001:2008 “Quality Management System – Requirements”;
[6] ISO/TC 176/SC 2/N 544R3 “ISO 9000 Introduction and Support Package: Guidance on the Concept and Use of the Process Approach for management systems” (2008)
[6] Davenport, T.H, & Short, J.E. (1990). The new industrial engineering: information technology and business process redesign. Sloan Management Review. 31. 11-27.