Difference between revisions of "Sharing"
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] NONAKA, I., TAKEUCHI, H. (1995) The knowledge-creating company. How Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation, Oxford University Press, Oxford. |
| + | |||
| + | [2] NONAKA, I. (2009). "Tacit Knowledge and Knowledge Conversion: Controversy and Advancement in Organizational Knowledge Creation Theory". Organization Science 20 (3): 635–652. | ||
| + | |||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
[[Portal:{{PAGENAME}}]] | [[Portal:{{PAGENAME}}]] | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 15 June 2014
Template:CommentContents
Definition
Sharing is The process of exchanging knowledge between individuals or organizations.
Summary
Sharing is one of the nine main knowledge process categories in the NKM Wiki.
For the nine main knowledge process categories see Fig 1.
Purpose
Knowledge sharing within the organization is mainly the question of sharing principle within the culture of the organization. The following elements of the culture must be taken in account:
- handling of professional jealousy of the experts;
- motivation — de-motivation of individuals;
- handling of the conflicts of interests between organization elements.
- The knowledge sharing possibilities are unique for the nuclear industry as compared to other competitive industries. By application of the knowledge sharing principle, the organizations are able to:
- Review best practices of others and adopt improvements based on benchmarking;
- Review of industry guidance, including operating experience and meet with peers from other companies at workshops and conferences;
- The sharing principle has also allowed experts from many companies to organize and meet regularly to refine and analyse approaches, develop and test performance measures and share the knowledge of best or good practices.
- Knowledge sharing deals with the levels of access of knowledge. Key aspects are:
- The methodical approaches;
- The potential of support from IT tools.
“Sharing is Additional work” Sharing inside the organization, and outside the organization (e.g. contractors) and on national or international level. IAEA Fast Reactor Knowledge Preservation, WANO Peer Reviews, GRS- knowledge sharing communities, CoP. The Integrated Management Systems are one of the key tools for sharing information- to write some sentences about it- Thomas+ examples
Source: National approaches and strategies for Nuclear Knowledge Management
Modes of knowledge sharing
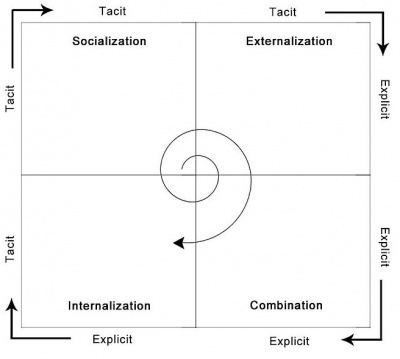
A famous early attempt at describing knowledge sharing and its implications for knowledge generation, the SECI-model [1][2] depicted in fig.1, has found wide diffusion and is still helpful in defining the different modes of knowledge transfer. In this model, four modes of knowledge transfer are identified:
- Tacit to tacit (Socialization): Knowledge is acquired by social interaction and is available as implicit knowledge
- Tacit to Explicit (Externalization): Implicit knowledge is captured, codified and thus transferred to explicit knowledge
- Explicit to Explicit (Combination): The newly acquired codified knowledge is combined with already available explicit knowledge
- Explicit to Tacit (Internalization): New knowledge is learned (internalized) and available as tacit knowledge, and may be transferred by socialization
Explicit and tacit knowledge thereby interact with each other in a continuous process. Knowledge, which is held by individuals as tacit knowledge, is shared with other individuals, groups or organizations, and interconnects to generate new knowledge. This process may be viewed as a "spiral" or an "amount" of knowledge, which grows as the four stages are repeatedly run through.
Sub-processes
The sub-processes for this process can be found in the Category:Sharing processes
Connection to other main categories
To see how this process is connected to KM challenges, benefits and tools and business processes, please refer to Portal:Sharing.
Contribution to the management system
Processes not in the management system
KM tools
For all the KM tools that help implement the knowledge process see Category:Sharing process tools
Case studies
References
[1] NONAKA, I., TAKEUCHI, H. (1995) The knowledge-creating company. How Japanese companies create the dynamics of innovation, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
[2] NONAKA, I. (2009). "Tacit Knowledge and Knowledge Conversion: Controversy and Advancement in Organizational Knowledge Creation Theory". Organization Science 20 (3): 635–652.
Related articles
Knowledge process (disambiguation)