Difference between revisions of "Retention plan"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{Clustering stage}} | {{Clustering stage}} | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
| − | |||
{{PAGENAME}} is {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | {{PAGENAME}} is {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | ||
| − | |||
'''Source: ''' [[Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations]] | '''Source: ''' [[Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations]] | ||
== Summary== | == Summary== | ||
| − | + | One paragraph summary which summarises the main ideas of the article. | |
| − | One | + | |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| − | + | Knowledge retention plans should be developed for [[Knowledge|knowledge]] and skills | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Knowledge retention plans should be developed for knowledge and skills | + | |
identified as most critical. Plans may include methods to retain the critical | identified as most critical. Plans may include methods to retain the critical | ||
knowledge and skills and actions necessary to mitigate the negative impact of | knowledge and skills and actions necessary to mitigate the negative impact of | ||
| Line 21: | Line 15: | ||
=== Options === | === Options === | ||
| − | A variety of alternatives can be used to address impending loss of critical | + | A variety of alternatives can be used to address impending loss of [[Critical knowledge|critical knowledge]] and skill. These include: |
| − | knowledge and skill. These include: | + | |
# Staffing: | # Staffing: | ||
#*New hire or transfer; | #*New hire or transfer; | ||
#*Current employee to assume responsibilities. | #*Current employee to assume responsibilities. | ||
| − | # Documentation and codification: | + | # Documentation and [[Codification|codification]]: |
#* New or revised procedures; | #* New or revised procedures; | ||
#*Checklists, inventories, etc.; | #*Checklists, inventories, etc.; | ||
#*Performance support systems; | #*Performance support systems; | ||
| − | #*Shared folders, intranet, job aids; | + | #*Shared folders, [[Intranet|intranet]], job aids; |
#*Videotaped instructions and demonstrations; | #*Videotaped instructions and demonstrations; | ||
#*Photographic records; | #*Photographic records; | ||
| − | #*Concept maps. | + | #*[[Concept map|Concept maps]]. |
| − | # Education and coaching: | + | # [[Education] and [[Coaching|coaching]]: |
| − | #*Classroom and simulator training; | + | #*Classroom and [[Training simulator|simulator training]]; |
| − | #*Computer based training, video based and alternative delivery; | + | #*[[Computer based training]], video based and alternative delivery; |
#*Directed self-study; | #*Directed self-study; | ||
#*On the job training and qualification; | #*On the job training and qualification; | ||
#*Targeted work assignments; | #*Targeted work assignments; | ||
| − | #*Coaching, shadowing and mentoring; | + | #*[[Coaching]], shadowing and [[Mentoring|mentoring]]; |
#*Apprenticeship programmes. | #*Apprenticeship programmes. | ||
# Process re-engineering: | # Process re-engineering: | ||
| Line 59: | Line 52: | ||
more widespread threat. To complete the knowledge retention plan or to | more widespread threat. To complete the knowledge retention plan or to | ||
address broader issues, coordination should occur with such groups as: | address broader issues, coordination should occur with such groups as: | ||
| − | |||
# Site training; | # Site training; | ||
# Other sites; | # Other sites; | ||
# Key leadership and succession planning; | # Key leadership and succession planning; | ||
# Peer teams; | # Peer teams; | ||
| − | # Recruitment; | + | # [[Recruitment]]; |
# Employee technical training and organizational effectiveness; | # Employee technical training and organizational effectiveness; | ||
# Process and methods; | # Process and methods; | ||
| Line 83: | Line 75: | ||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
| + | [[retention]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Attrition]] | [[Attrition]] | ||
Revision as of 08:53, 21 August 2013
Contents
Definition
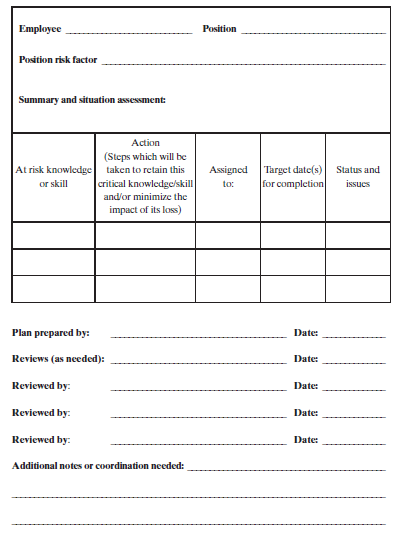
Retention plan is A plan that identifies the critical knowledge and positions in an organization, and methods to be used for addressing potential knowledge loss through attrition, and the process that will ensure that the plan is continually updated to meet changing business needs Source: Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations
Summary
One paragraph summary which summarises the main ideas of the article.
Description
Knowledge retention plans should be developed for knowledge and skills identified as most critical. Plans may include methods to retain the critical knowledge and skills and actions necessary to mitigate the negative impact of losing the knowledge and skills.
Options
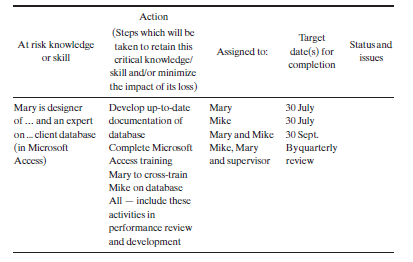
A variety of alternatives can be used to address impending loss of critical knowledge and skill. These include:
- Staffing:
- New hire or transfer;
- Current employee to assume responsibilities.
- Documentation and codification:
- New or revised procedures;
- Checklists, inventories, etc.;
- Performance support systems;
- Shared folders, intranet, job aids;
- Videotaped instructions and demonstrations;
- Photographic records;
- Concept maps.
- [[Education] and coaching:
- Classroom and simulator training;
- Computer based training, video based and alternative delivery;
- Directed self-study;
- On the job training and qualification;
- Targeted work assignments;
- Coaching, shadowing and mentoring;
- Apprenticeship programmes.
- Process re-engineering:
- Process improvement;
- Update equipment;
- ‘Smart’ tools and technology;
- Task, product or service termination.
- Alternative or shared resources:
- Agency/site/department expert;
- Rotational or ‘visiting’ staff;
- Multiple skills, cross-training, collateral duties;
- Contractors, part-timers, retirees.
Coordination
Some actions included in knowledge retention plans need to be coordinated with other groups in order to be completed. In other instances, a potential knowledge loss issue at one site or within one group may suggest a more widespread threat. To complete the knowledge retention plan or to address broader issues, coordination should occur with such groups as:
- Site training;
- Other sites;
- Key leadership and succession planning;
- Peer teams;
- Recruitment;
- Employee technical training and organizational effectiveness;
- Process and methods;
- Corporate office.
This coordination should be addressed as part of the development of the knowledge retention plan. As needed, senior management addresses coordination or implementation issues, which cross major sites or divisions.
Source: Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Industry Organizations
References
[1]