Difference between revisions of "Asset management"
(→Description) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
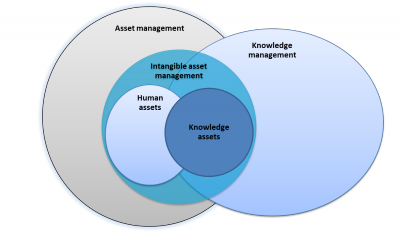
Asset management is an approach for management of a [[Nuclear organization|nuclear organization]]| to consider, in a balanced fashion, the entirety of its resources. These include tangible assets such as personnel and other animate creatures, facilities, equipment, fiscal investment, inventory, and [[Intangible asset|intangible assets]] such as [[Knowledge|knowledge]], see Fig 1. | Asset management is an approach for management of a [[Nuclear organization|nuclear organization]]| to consider, in a balanced fashion, the entirety of its resources. These include tangible assets such as personnel and other animate creatures, facilities, equipment, fiscal investment, inventory, and [[Intangible asset|intangible assets]] such as [[Knowledge|knowledge]], see Fig 1. | ||
| − | As [[Knowledge management]] concerns itself with knowledge, at least part of which is organization's intangible asset, KM and asset management partly overlap. | + | As [[Knowledge management]] concerns itself with knowledge, at least part of which is organization's intangible asset, KM and asset management partly overlap, see Fig 1. |
Approaches such as the [[Balanced scorecard|balanced scorecard]] can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. Also a well-planned [[KM system]] can contribute to meeting such challenges. | Approaches such as the [[Balanced scorecard|balanced scorecard]] can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. Also a well-planned [[KM system]] can contribute to meeting such challenges. | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 23 April 2014
Definition
Asset management is Management of organization's assets
Summary
Description
Asset management is an approach for management of a nuclear organization| to consider, in a balanced fashion, the entirety of its resources. These include tangible assets such as personnel and other animate creatures, facilities, equipment, fiscal investment, inventory, and intangible assets such as knowledge, see Fig 1.
As Knowledge management concerns itself with knowledge, at least part of which is organization's intangible asset, KM and asset management partly overlap, see Fig 1.
Approaches such as the balanced scorecard can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. Also a well-planned KM system can contribute to meeting such challenges.