Difference between revisions of "Knowledge process"
(→Summary) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Summary== | == Summary== | ||
knowledge processes includes knowledge production and integration activities with sub processes like acquiring, transforming, developing, disseminating, using, sharing and preserving knowledge as a way to meet specified internal demand that can ultimately improve orgaizational learning. In this regard, knowledge processes helps an organization to gain insight and understanding from its best practices. | knowledge processes includes knowledge production and integration activities with sub processes like acquiring, transforming, developing, disseminating, using, sharing and preserving knowledge as a way to meet specified internal demand that can ultimately improve orgaizational learning. In this regard, knowledge processes helps an organization to gain insight and understanding from its best practices. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 09:48, 24 September 2013
Definition
Knowledge process is Knowledge process is a process that acts on /or with knowledge, either individual knowledge or organizational knowledge. Source: [[]]
Summary
knowledge processes includes knowledge production and integration activities with sub processes like acquiring, transforming, developing, disseminating, using, sharing and preserving knowledge as a way to meet specified internal demand that can ultimately improve orgaizational learning. In this regard, knowledge processes helps an organization to gain insight and understanding from its best practices.
Description
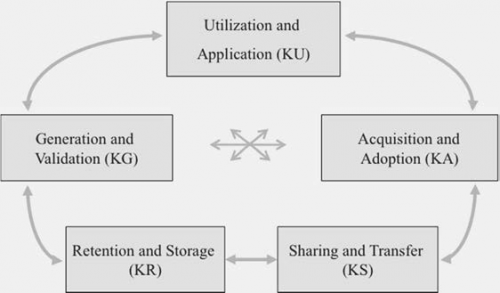
In the literature, authors such as N.T. Pham and F.W. Swierczek [1] describe the mechanisms by which knowledge is accumulated, disseminated and stored in organizations and many refer to these as knowledge processes. There are many different definitions of knowledge processes used in the literature. This research classified the more widely used and accepted definitions into one of five primary knowledge processes, shown below in Figure 1. The primary knowledge processes are defined as [2]:
- Knowledge acquisition and adoption;
- Knowledge generation and validation;
- Knowledge sharing and transfer;
- Knowledge retention and storage; and
- Knowledge utilization and application.
Knowledge processes can be viewed as the means by which organizations build, maintain and apply the tacit and explicit knowledge in all its various forms.
References
[1] PHAM, N.T., SWIERCZEK. F.W., Facilitators of organizational learning in design, The Learning Organization, 13, 2, (2006) 186–201.