Difference between revisions of "Intangible asset"
(→Management of intangible assets) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Description== | == Description== | ||
| − | International Accounting Standards Board standard 38 (IAS 38) defines an intangible asset as | + | International Accounting Standards Board standard 38 (IAS 38) defines an intangible asset as non-monetary asset without physical substance but can be identified [1]. Intangible assets of an organization are the part of its assets which are not in physical form and do not have an obvious physical value. Intangible assets do not define organization's current market value like tangible assets. However, intangible assets can be critical to organization's long-term success or failure and define its future value. |
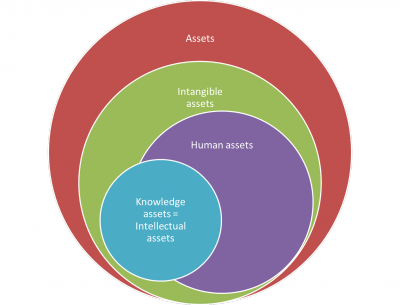
As depicted in Fig 1, intangible assets include [[Human asset|human]] and [[Knowledge asset|knowledge assets]]. In addition, the reputation of the organization, its [[Intellectual property|intellectual property]], copyrights, patents, [[Business process|business processes]], [[Culture|culture]] and trade marks are part of its intangible assets. | As depicted in Fig 1, intangible assets include [[Human asset|human]] and [[Knowledge asset|knowledge assets]]. In addition, the reputation of the organization, its [[Intellectual property|intellectual property]], copyrights, patents, [[Business process|business processes]], [[Culture|culture]] and trade marks are part of its intangible assets. | ||
Revision as of 10:24, 8 June 2014
Template:Consolidation stage,Contents
Definition
Intangible asset is A non-physical asset of an organization
Source: Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations
Summary
Description
International Accounting Standards Board standard 38 (IAS 38) defines an intangible asset as non-monetary asset without physical substance but can be identified [1]. Intangible assets of an organization are the part of its assets which are not in physical form and do not have an obvious physical value. Intangible assets do not define organization's current market value like tangible assets. However, intangible assets can be critical to organization's long-term success or failure and define its future value.
As depicted in Fig 1, intangible assets include human and knowledge assets. In addition, the reputation of the organization, its intellectual property, copyrights, patents, business processes, culture and trade marks are part of its intangible assets.
Human asset
Knowledge asset
Intellectual property
Business processes
Culture
Management of intangible assets
Intangible assets are managed as part of an organisation's asset management. In addition, IAS 38 Intangible Assets outlines the accounting requirements for intangible assets.
Management areas involved with intangible assets include
References
[1] http://www.ifrs.org/The-organisation/Pages/IFRS-Foundation-and-the-IASB.aspx