Difference between revisions of "Knowledge retention"
(→Related Articles) |
(→Related Articles) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Related Articles== | ==Related Articles== | ||
| − | [[Ageing | + | [[Ageing workforce]], [[Retention]]. [[Retention plan]], [[Capture]] |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 1 December 2015
Definition
Knowledge retention is
Description
Knowledge Retention addresses the case of knowledge leaving the organization. For some organizations this is a more serious problems than for others. Knowledge leaves organizations for many reasons, although for many organizations the problem is an ageing/retiring workforce and the need to identify what knowledge needs to be retained within the organization, but knowledge leaves because of lay-offs and normal staff turn-over too.
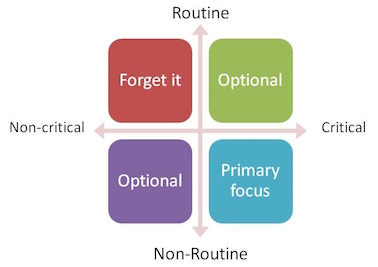
It is not necessary to save all of the knowledge that exists within an organization, although some people want to, but some knowledge is transient and/or not critical to the organization's operations, so trying to save it all creates overload, noise, and confusion. It is much better to review the knowledge and make an assessment of what is critical vs. non-critical and routine vs. non-routine, then a decision can be made as to how to best deal with retaining it (or not).
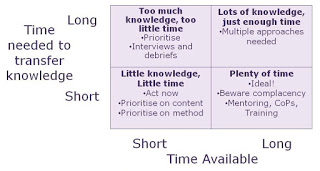
Once the determination has been made as to what is important to retain the organization can assess the time needed to transfer knowledge, vs. the time available. The diagram below suggests some knowledge management activities to help the organization capture the necessary knowledge, the rest can be forgotten.
Related Articles
Ageing workforce, Retention. Retention plan, Capture