Difference between revisions of "Workforce planning"
DavidBeraha (Talk | contribs) (→Definition) |
|||
| (78 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{David}} |
| − | + | <!-- | |
| + | {{Consolidation stage}}, | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Priority}}, |
| + | --> | ||
| + | ==Definition== | ||
| + | {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | ||
| + | <!-- '''Source: ''' [[Planning and Execution of Knowledge Management Assist Missions for Nuclear Organizations]] --> | ||
== Summary== | == Summary== | ||
| − | + | The IAEA estimates future nuclear electricity generating capacity in the world. The number of operating nuclear reactors is projected to increase by about 90 by 2030 from the total of 437 reactors at the end of 2013. The purpose of this article is to provide member states and organizations with methodology to understand the role of Workforce Planning for ensuring safe, reliable and efficient nuclear facility operations. For a country that does not already have nuclear power, and even for those wishing to significantly expand an existing nuclear energy capability, it may take up to 10–15 years to develop the necessary infrastructure. This article will provide knowledge how the essential elements of a Workforce Planning Program for existing and new NPP's. | |
| − | == | + | == Workforce Development Approach == |
| + | [[File:1248_fig01.png|400px|thumbnail|right|FIG. 1. Strategic approach for workforce development.]] | ||
| + | Strategic approach for workforce development means systematic process of interconnection between economic and safety goals of NPP with organizational [[Knowledge asset|knowledge asset]] which is provided by sufficient qualified workforce. | ||
| − | + | Many nuclear organizations recognize that a strategic approach is most effective in addressing the broad array of workforce issues, which many organizations face. While this publication focuses on managing the risk associated with potential [[Knowledge loss|loss of nuclear knowledge]], the interactions between KM and other HR development programmes should be considered. These programmes may include the following: | |
| − | '''Source:''' [[Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear | + | # Workforce planning; |
| + | # [[Recruitment|Recruiting]] initiatives; | ||
| + | # Talent acquisition initiatives; | ||
| + | # Training programmes; | ||
| + | # [[Succession planning]] and [[Leadership development|leadership development]]; | ||
| + | # [[Knowledge management]]; | ||
| + | # Organizational [[Competency management|competency management]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The concept of strategic approach for workforce development is shown on Figure 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Knowledge loss risk management as a process of [[Knowledge management|KM]] find its place in the context of workforce development as a systematic process for identifying gaps in organizational competency due to potential staff attrition. After evaluation of the knowledge loss threats, action plan should be developed to mitigate the risks. | ||
| + | For example, if a potential for [[Knowledge loss|knowledge loss]] is identified involving a plant expert, solutions may involve a [[Recruitment|recruiting]] initiative and/or developing a formal [[Training|training]] module. The pending retirement of an experienced component engineer may require recruiting, training, and succession planning. There are numerous other examples where an integrated, strategic approach is taken to ensure the overall effectiveness of nuclear programmes. More detail HR workforce planning approach is in IAEA publication [1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:1248_fig02.png|400px|thumbnail|right|FIG. 2. Knowledge Management Cycle.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As part of workforce planning, knowledge transfer and retention begins at the time of hire and moves through the employee life-cycle. General life-cycle of knowledge transfer for the nuclear specialist is shown on a Figure 2. Newly hired employees complete required initial training for their positions as part of new-hire orientation and assimilation. Many positions require certification and/or qualifications through extensive, formalized training programmes. Upon completion of those programmes, employees qualified to perform their tasks are considered ‘independent’ workers. These individuals are capable of performing their jobs; however, they may not be as proficient as an expert, long-term employee. Through the effective use of knowledge management, managers can accelerate a newer employee’s technical capabilities and can help transfer critical/unique knowledge. Important role in workforce development plays KM culture. Establishment of motivation mechanisms to encourage highly qualified staff to share knowledge and skills are very important for the reason that knowledge sharing culture supports safety culture. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- '''Source:''' [[Practical Approaches to Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Organizations]] --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Workforce Planning For New Nuclear Power Programmes == | ||
| + | ===Analysis of infrastructure activities, competencies and resource requirements=== | ||
| + | As indicated earlier, a prerequisite for developing a workforce plan to support a national nuclear power programme is to clearly define in Phase 1 (considering the feasibility of nuclear power for the country) the roles, responsibilities and functions of all the stakeholder organizations to be involved. As the programme progresses into | ||
| + | Phase 2, this is likely to include, as a minimum, the NEPIO, an independent regulatory body and a designated operating organization. The workforce planning process can then be used to identify the major activities that need to be undertaken to achieve the milestones, which organizations should be responsible for these activities, and the | ||
| + | competencies needed. A part of this process will be to determine which of these activities are within the current national capability, which could be undertaken nationally in the longer term (with training and support) and which should be contracted out from the outset. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to the nuclear related activities of a nuclear energy programme, as with all major capital projects, | ||
| + | significant non-nuclear resources will be needed, particularly in the early construction stages of the programme. For | ||
| + | general guidance on workforce development for the implementation of a nuclear energy programme, Member | ||
| + | States may find the IAEA publication on Manpower Development for Nuclear Power: A Guidebook [9] useful. | ||
| + | Although this publication, issued in 1980, was based on the previous generation of nuclear energy programmes, much of the content is still relevant. For more detailed workforce planning, the main IAEA publications providing useful guidance are listed in Table 6 at the end of this section, indicating those organizations and the phases to which they are most applicable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The workforce planning process for a specific nuclear energy programme should begin with a review of the | ||
| + | activities identified under each of the 19 infrastructure issues, phase by phase (as identified in Ref. [1]), which | ||
| + | should form the basis for an initial analysis of competence and resource needs. It is important to remember, | ||
| + | however, that although the infrastructure issues have been separated into 19 discrete topics, in reality the activities | ||
| + | associated with these topics are often integrated and interdependent. The same individuals may be engaged in | ||
| + | various activities covering several infrastructure issues. Hence, for workforce planning purposes, it is more | ||
| + | appropriate to consider these activities in terms of organizational responsibilities. In some cases, it is clear where | ||
| + | responsibilities should be assigned for particular activities; in others, it will be a judgement based on the particular | ||
| + | national organizational arrangements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During Phase 1, the NEPIO is likely be the major responsible organization and, in addition to the information | ||
| + | contained in the Milestones publication, an overview of its functions and responsibilities during Phase 1 is provided | ||
| + | in Table 2, taken from Ref. [2]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During Phase 2, the regulatory body and operating organization will be assigned (assuming they were not | ||
| + | already assigned in Phase 1), and responsibilities, and therefore resource requirements, will progressively be | ||
| + | transferred to these organizations. Table 3 [2] provides an overview of the NEPIO’s functions and responsibilities | ||
| + | during Phase 2, and a similar overview of the responsibilities of the operating organization during Phase 2 is | ||
| + | included in Table 4 (taken from Ref. [3]). Useful sources when developing workforce plans for the regulatory body | ||
| + | include Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities [10] and Training the Staff of the | ||
| + | Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities: A Competency Framework [11]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the beginning of Phase 3, the major workforce planning effort is likely to be focused on the operating | ||
| + | organization in order to adequately resource, first, the commissioning and, subsequently, the operation of the NPP. | ||
| + | Table 5 provides a summary of the responsibilities of the operating organization during Phase 3. The IAEA | ||
| + | publication Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource Considerations [12] contains | ||
| + | guidance for planning purposes. Inputs for workforce planning for the organizational and resourcing requirements | ||
| + | of the operating organization to actually operate the plant, will depend, to some extent, on the design of the NPP | ||
| + | selected. It is likely that the vendor of the chosen design will have recommendations in this area. Member States | ||
| + | may find broader guidance on the recruitment, training and qualification of these staff in Refs [13, 14]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | TABLES 1-6 not Wikified. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Prerequisites for workforce planning (Phase 1)=== | ||
| + | As stated previously, a prerequisite for effective workforce planning for a nuclear power programme is the | ||
| + | establishment of clear roles, responsibilities and functions for all of the organizations that will have a role in | ||
| + | considering a nuclear power programme. Absent these roles, responsibilities and functions, there is no | ||
| + | framework/basis for workforce planning. The establishment of a NEPIO as described in Ref. [2] is one way in | ||
| + | which to effectively develop these roles, responsibilities and functions, as well as to foster coordination among | ||
| + | those organizations involved in considering a nuclear power programme. However, these roles, responsibilities and | ||
| + | functions can certainly be determined without having a NEPIO in place. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Developing a workforce plan=== | ||
| + | Summarizing the foregoing, for every country developing a nuclear energy programme, the workforce plans will be different, based on factors such as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Scope (and main purpose) of the construction build programme; | ||
| + | *Nature of construction build programme (fully turnkey versus transition to indigenous construction) and subsequent relationship with the vendor; | ||
| + | * Availability of nuclear expertise from non-energy applications (industry, medical, agriculture, applied sciences); | ||
| + | *Access to available international nuclear expertise; | ||
| + | *Existing (if any) nuclear educational programmes; | ||
| + | *Availability and quality of non-nuclear workforce. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The quantity and variety of resources needed to establish a nuclear energy programme can be phased in over the development of the programme and can begin with quite small numbers. For example, the owner/operator project team needed to manage the specification and contracting of the first NPP during Phase 2 may be as few as 30–35 personnel (assuming a turnkey project where the supplier has overall responsibility for management of | ||
| + | construction and commissioning). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Overview==== | ||
| + | Workforce planning is an essential, ongoing [[Human resource management|human resources management]] process. Each organization | ||
| + | involved in the nuclear energy programme should develop and maintain its own workforce plan; at least for | ||
| + | Phases 1 and 2, the NEPIO should maintain an overall plan to enable an integrated national approach to resource | ||
| + | utilization and development. In developing the national workforce plan, it is important to gain an understanding of | ||
| + | how the workflow, and therefore the required resources and associated competencies, evolve as the programme | ||
| + | develops: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *During Phase 1, the NEPIO will be responsible for most of the activities being undertaken. The number of staff involved will be relatively small and individuals may be drawn from various government departments, with much of the actual specialist work being done by external experts/expert groups. The work to be undertaken during Phase 1 will range from the development of recommendations concerning national policy in some areas through to more detailed analysis in others. Thus, some staff will be working at quite a high level, while others will be involved in more detailed activities (as stated earlier, Ref. [2] deals with the establishment and specific responsibilities of the NEPIO). | ||
| + | * At the beginning of Phase 2, the NEPIO will still be driving the programme, but the other key responsible organizations, including the regulatory body and the owner/operating organization, should be fully established and taking an increasingly active role. The core project team for the construction of the plant should be in place, as even at this early stage there will be a wide variety of activities to be managed, and early recruitment of those operations staff with long training lead times (see Section 5.4) should be under way. | ||
| + | Towards the end of Phase 2, the NEPIO should have handed over many of its early responsibilities to the various responsible organizations and may indeed be considered to have completed its responsibilities. | ||
| + | * By the beginning of Phase 3, although the NEPIO may still have an oversight/coordination role, especially if the first NPP is part of a bigger programme, primary responsibility for management of NPP construction and commissioning should be with the operating organization. The regulatory body will be actively engaged in the licensing of the site and plant design as well as overseeing manufacturing and construction, as appropriate. The operating organization will be actively recruiting and managing the training of its permanent plant staff. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This profile of resource requirements is illustrated in Fig. 3. From an education/qualification perspective, | ||
| + | during Phases 1 and 2 of infrastructure development, the majority of the core staff needed will be at the | ||
| + | professional/graduate level. However, when staffing the NPP for the operations phase, the graduate component is | ||
| + | generally the minority part of the total workforce, with the majority of the workforce being ‘technician’ level staff | ||
| + | (i.e. staff who may only have high school level educational qualifications, coupled with some form of vocational | ||
| + | skill certification and/or apprenticeship. These staff will require less ‘nuclear’ knowledge than their graduate | ||
| + | counterparts but will need considerable training in order to understand the quality and safety requirements of | ||
| + | working in a nuclear environment and why nuclear is different from other engineering and industrial environments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Typical phasing of resource requirements.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 3. Typical phasing of resource requirements]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====[[Recruitment|Recruitment considerations]]==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Considerations for staffing a nuclear energy programme=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Overall approach==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | National [[Recruitment|recruitment]] processes and practices vary from country to country and may have a significant impact | ||
| + | on the workforce planning process. However, nuclear energy programmes require staff of the highest calibre, and it | ||
| + | is common practice for educational and/or qualification/licensing requirements to specified by the regulatory body, | ||
| + | at least for certain safety related roles. It may therefore be necessary to implement a specific process for the | ||
| + | recruitment of staff. Depending on the national [[Education|education]] capability, some organizations are able to recruit their | ||
| + | professional talent directly at the graduate level by a competitive process that may result in several hundred | ||
| + | candidates applying for one or more jobs. This then requires screening to select perhaps 6–10 candidates for | ||
| + | interview, which is a time consuming and resource intensive process. At the other extreme, some countries establish | ||
| + | nuclear ‘academies’ or universities and select students directly from secondary education with the expectation that | ||
| + | the vast majority of ‘graduates’ from these establishments will be employed directly by the industry, thereby | ||
| + | simplifying the ‘recruitment’ process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is good practice to set limits on the duration of the recruitment process, from the announcement of a job | ||
| + | opportunity to the day of appointment. This might be days or months, depending on whether the job is at a support | ||
| + | staff or professional level, but it sets expectations on the part of both the recruiting organization and the applicants. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another important consideration related to the duration of the recruitment process is the scope and duration of | ||
| + | any job related training considered necessary prior to an individual’s being authorized to undertake his or her | ||
| + | allocated duties. This may range from a few weeks of familiarization for an experienced technical specialist | ||
| + | working narrowly within his or her field to several years for a plant operator who may only have secondary | ||
| + | education level qualifications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hence, for some positions (e.g. operations, reactor engineering, radiological safety and training), it will be | ||
| + | necessary to begin the recruitment process several years prior to the individual’s being needed to undertake his or | ||
| + | her duties, even prior to signing the contract for the plant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In an area where several Member States are considering implementing a nuclear energy programme, one | ||
| + | practical approach might be to establish a regional training centre (RTC), thus sharing the burden as well as the | ||
| + | benefits of specialist nuclear training among several Member States. There are a number of potential benefits in | ||
| + | developing an RTC, including: | ||
| + | *Set-up as well as running costs are shared between several Member States. | ||
| + | *An RTC avoids competition between individual Member States in trying to attract scarce specialist resources to provide nuclear training. | ||
| + | *RTCs are more likely to attract the support of international organizations, such as the IAEA, and are more likely to be able to establish links/partnerships with other international training/educational institutions, operating organizations and suppliers. | ||
| + | * Member States may be less likely to lose staff to neighbouring countries if the whole region has adequate access to such specialist training resources. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Such RTCs where staff can receive training would be particularly beneficial during the early phases of a nuclear energy programme, before there is an operating NPP or even an NPP construction project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An essential element of developing competence is the need to gain practical training and experience. Some | ||
| + | elements of this are discussed in the next section, but, inevitably, it will be necessary to find a means of placing | ||
| + | some personnel within existing nuclear operating organizations. The existence of an RTC and the possibility of such | ||
| + | a facility establishing international links may also be of benefit in this respect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Phase 1==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The initial resourcing of Phase 1 presents a major challenge in workforce planning, as a Member State is | ||
| + | unlikely to have all or even many of the needed competencies, particularly those relating to nuclear power. Even | ||
| + | starting with a zero baseline, the staff required for Phase 2 will have had the opportunity to develop their initial | ||
| + | competence during Phase 1, and similarly for Phase 3. Hence, building competence during Phase 1 is vital for the | ||
| + | success of the subsequent phases. An essential component of building that competence is giving staff real | ||
| + | experience at the earliest possible opportunity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One way of providing staff with the opportunity to gain experience during Phase 1 is to adopt a combined | ||
| + | approach of importing international expertise to support the overall programme, while at the same time placing | ||
| + | national staff overseas to gain experience. This approach may usefully be adopted by all responsible organizations: | ||
| + | the NEPIO, regulatory body, operating organization, national industrial organizations hoping to participate in the | ||
| + | manufacturing and/or construction of the plant, academic institutions involved in the development of national | ||
| + | capability in the medium to long term, and those scientific/research and technical support organizations which may | ||
| + | provide services to the plant throughout its life cycle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | External expertise has been successfully used in a number of different ways, for example: | ||
| + | * Contracting out whole work packages to experienced consultants, but including requirements to utilize/train national staff in delivering the work package (where little or no national competence exists in the particular area); | ||
| + | * Contracting with consultants to become ‘temporary’ staff working with nationals to deliver work packages, adding value in the more complex areas while developing national staff (where a modest level of competence exists); | ||
| + | *Engaging senior consultants to ‘coach’ national staff in specific areas of competence (where a higher level of national capability exists); | ||
| + | *Organizing national conferences/workshops where vendors and specialist support organizations can present their capabilities and services (care needs to be taken to ensure that no suggestion of preference or commitment to future business is implied). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, there are a variety of ways in which staff can be given the opportunity to build competence and experience overseas: | ||
| + | *Establishing bilateral and multilateral relationships with governments, regulatory agencies, vendors, utilities, educational institutions and others, which allow for placements and staff ‘swapping’; | ||
| + | *IAEA training courses, fellowships and internships; | ||
| + | *Formal courses of overseas study (e.g. vocational, undergraduate and postgraduate programmes, which may include industry assignments) and training (directly with utilities/national nuclear training organizations); | ||
| + | * Building staff training and development assignments into potential contracts with vendors, consultants, service providers, etc.; | ||
| + | * Developing ‘strategic alliances’ with vendors/equipment suppliers whereby national organizations obtain licenses to manufacture components in-country, which can include training and qualification in the country of origin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fortunately, the number of staff directly involved in Phase 1 is relatively small, maybe only 20–30 people, | ||
| + | although this number would require the additional support of expert groups, either nationally or internationally. | ||
| + | Most, if not all, of these staff will be within the NEPIO, and these staff are likely to be heavily supported by | ||
| + | national/international expertise. An example of how this group might be organized is illustrated in Fig. 4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Example of the organization of a NEPIO in Phase 1.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 4. Example of the organization of a NEPIO in Phase 1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | If a Member State has an existing regulatory body for non-energy applications, this group can be used to | ||
| + | undertake the initial work relating to the establishment/revision of legal and regulatory requirements for nuclear | ||
| + | energy during Phase 1, even if a separate regulatory body for nuclear energy is to be established in due course. | ||
| + | |||
| + | While it may be difficult to make any long term staffing decisions prior to a formal decision on whether to | ||
| + | proceed with a nuclear energy programme at Milestone 1, due to the constraints of the recruitment and training | ||
| + | requirements described above, consideration should be given to commencing recruitment of some key staff during | ||
| + | Phase 1, to be available for work in Phase 2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Phase 2==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This will be a very busy and diverse period in terms of workforce planning and staff recruitment, and so it is | ||
| + | easier to address each of the three main groupings separately. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Nepio===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The staffing of the NEPIO will peak during this phase, as can be seen in Fig. 5, typically in the range on | ||
| + | 20–50 staff members, depending of the level of specialist support available. By the end of Phase 2, many of their | ||
| + | responsibilities should have been transferred to the other responsible organizations, especially the regulatory | ||
| + | body and the operating organization. Depending on the size of the nuclear energy programme, the NEPIO may | ||
| + | cease to exist as such (or its role may shift to one of purely coordination), with some of its oversight | ||
| + | responsibilities (and resources) being transferred to the appropriate regulatory agencies and others being placed | ||
| + | within those government departments which would normally be responsible for such activities. In addition, | ||
| + | based on the experience they have gained, key NEPIO staff may be transferred into senior positions in the | ||
| + | operating organization, either within the nuclear plant management structure (single NPP) or in the corporate | ||
| + | organization (multi-unit programme). It is important however that, even if the NEPIO ceases to exist as an | ||
| + | organization, the government continues to demonstrate its commitment to, and support for, the nuclear energy | ||
| + | programme, and that key individuals within the appropriate government departments have the authority and | ||
| + | responsibility to continue promoting the programme. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Example of phasing of resource requirements for a NEPIO.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 5. Example of phasing of resource requirements for a NEPIO]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Regulatory body===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The development of the work processes, human resources and competencies of the independent regulatory | ||
| + | body is a high priority task in Phase 2 and will continue through Phase 3. During Phase 2, the regulatory body will | ||
| + | be proposing and promulgating safety regulations and guides, as well as adopting appropriate industrial codes to | ||
| + | properly cover all foreseen nuclear activities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The number of staff of the regulatory body will depend on two key factors: | ||
| + | *The number of organizations available to provide technical support to the regulatory body (Section 2.2); | ||
| + | *The regulatory approach adopted by the Member State (Section 2.4). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Typically, the regulatory body may have a core staff of about 40–60 people with the competencies to develop | ||
| + | or adopt safety regulations, develop and implement an authorization process, review and assess the safety and | ||
| + | design documentation provided by the operating organization against the adopted regulations, and inspect the | ||
| + | facility, the vendor and manufacturers of safety related components. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Peak numbers within the regulatory body may be higher, for example, up to 100–150 personnel, again | ||
| + | dependent on the level of specialist independent support available and on the number of NPPs planned (workload). | ||
| + | In the case of only one plant, these numbers should decline over commissioning, as illustrated in Fig. 6. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Phasing of resource requirements for the regulatory body.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 6. Phasing of resource requirements for the regulatory body]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | It is generally accepted that regulatory bodies should have competencies in four main areas: | ||
| + | *Legal basis and regulatory processes; | ||
| + | *Technical disciplines; | ||
| + | *Regulatory practices; | ||
| + | *Personal and interpersonal competencies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Detailed guidance on the development of these competencies for regulatory body staff may be found in | ||
| + | Ref. [11], and the IAEA can provide assistance in this area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Operating organisation ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Purely from an operational point of view, the planning and recruitment of the staff that will eventually operate | ||
| + | the plant needs careful consideration at an early stage in the programme for the following reasons: | ||
| + | *The number of staff required is much larger than for the other organizations, typically in the range of 500–1000 for a single or twin unit plant, up to several thousand for a multiple unit plant (see Section 5.4). | ||
| + | *Many of the operating organization staff have safety related roles as described above, requiring authorization, and hence have significant training programmes, required up to several years for completion (much of such training may be initially conducted at reference plant(s) overseas). | ||
| + | *The commissioning of an NPP, especially if it is a country’s first plant, presents a unique opportunity for staff to gain practical experience. For those staff with specific responsibilities during the commissioning phase, their initial training must be completed. For other staff who do not have specific responsibilities, the commissioning phase still provides opportunities to observe activities and gain practical experience. For these | ||
| + | staff to gain maximum benefit and to avoid resource conflict, at least initial classroom training should be completed prior to the main commissioning phase. The IAEA publication Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource Considerations [12] provides guidance in this area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition, for a first NPP, there are many other activities to be carried out by the future operating | ||
| + | organization, such as: | ||
| + | * Preparing the BIS; | ||
| + | *Preparing the environmental impact assessment report (EIAR); | ||
| + | *Establishing interfaces with the various national and international bodies associated with safeguards, security, physical protection, the nuclear fuel cycle and radioactive waste; | ||
| + | *Establishing the integrated management system needed to ensure the safe operation of the plant; | ||
| + | * Creating the foundations of an appropriate safety culture prior to commencing construction; | ||
| + | *Preparing a strategy for dealing with the public; | ||
| + | *Starting to prepare emergency plans and procedures; | ||
| + | *Other (see Ref. [3]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to ensure that there are enough competent staff available for these activities, it will be necessary to | ||
| + | begin the recruitment and training of operating organization staff early in Phase 2 (see Fig. 7). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Buildup of plant staff prior to commissioning.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 7. Buildup of plant staff prior to commissioning]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Phase 3==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | By the beginning of Phase 3, the majority of NEPIO staff is likely to have either transferred to one of the other | ||
| + | responsible organizations or returned to one of the government departments with ongoing responsibility for the | ||
| + | nuclear energy programme. The majority of regulatory body staff should be in place, undertaking training and | ||
| + | discharging their responsibilities in respect of the licensing process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A project team should be established within the operating organization and fully staffed and competent to | ||
| + | meet its responsibilities. This team will oversee the project on behalf of the Member State/operating organization, | ||
| + | as distinct from the vendor established project management team (PMT), which will manage the actual construction | ||
| + | of the NPP and which may include representatives of the operating organization [3]. It is recommended that this | ||
| + | team is part of the operating organization in order to retain their experience and expertise, although different | ||
| + | practices may be found in different countries. This also depends on the size of the nuclear energy programme. A key | ||
| + | issue here is to ensure that senior PMT staff are not also designated to be senior plant operations staff, as their | ||
| + | project management responsibilities during commissioning are likely to conflict with the opportunities for | ||
| + | operations staff to gain unique hands-on experience during the commissioning phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Plant staff===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | During this phase, the majority of the plant operating staff, especially technical staff, should be recruited and | ||
| + | fully trained. In reality, the actual staff numbers required will vary from plant to plant. This is even true in Member | ||
| + | States currently operating many NPPs. This can be for a variety of reasons, including: | ||
| + | *Stand-alone NPP or part of a fleet of NPPs with one operating organization and entralized support functions; | ||
| + | *Regulatory requirements specified by the Member State’s national nuclear regulator; | ||
| + | *Regulatory requirements specified within the Member State by provincial regulators; | ||
| + | *Minor differences in design, even on twin/multi-unit sites; | ||
| + | *Concept of operations, including the level of plant automation and control, and approach to maintenance (in-house staff, joint maintenance by operating utility staff or external contractors); | ||
| + | *Physical attributes of the NPP — physical layout of plant systems/equipment; | ||
| + | *Local labour conditions; | ||
| + | *National/local laws/regulations on labour and employment practices; | ||
| + | *Support relationships with vendors/suppliers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To give readers of this publication a better understanding of the staffing needed by the end of Phase 3 for the | ||
| + | operating organization (the largest of the nuclear organizations to be established), Appendix I provides an example | ||
| + | of the median staffing levels by function for some 67 one-unit and two-unit NPPs in operation in North America | ||
| + | and western Europe (see notes in the appendix), giving totals of approximately 700 for a single unit plant and 1000 | ||
| + | for a twin unit. A description of each of the functions is included in Appendix II for clarity. It must be emphasized | ||
| + | that these figures are presented as examples only, as actual numbers will depend on many factors, including those | ||
| + | listed above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should be emphasized that these numbers relate to direct plant staff only. If more than one NPP is to be built, | ||
| + | it is likely that a central or ‘headquarters’ function will be established with its own resource requirements, which in | ||
| + | turn may impact the numbers required on each unit if some of the functions are centralized (e.g. design authority, | ||
| + | technical support, maintenance, finance, procurement). Additional comparative data on staffing numbers can be | ||
| + | found in Ref. [15]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The phasing of recruitment of plant staff depends greatly on their training lead times (how long they need for | ||
| + | formal training prior to authorization/certification for their duties), and these vary greatly, depending on their roles | ||
| + | and responsibilities. Figure 7 provides an example of the phasing of recruitment in years before commissioning, | ||
| + | based on the totals given above. An example breakdown of qualification and training requirements (including | ||
| + | typical training lead times, based on the stated expected entry-level education requirements) for various functions at | ||
| + | a typical US NPP is included in Appendix III. The reader is cautioned that such lead times will vary considerably | ||
| + | based upon national norms and regulations regarding factors such as education, vocational training, labour laws and | ||
| + | practices, and industry practices. This variability underlines the need for each country to analyse its own situation | ||
| + | and needs through its detailed workforce planning. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In terms of staffing a first nuclear plant, a number of options have been used, including: | ||
| + | *Initial operation by a national staff, which is already trained by the vendor but under the supervision of an experienced vendor supplied staff for an initial period; | ||
| + | *An initial period of operation staffed by the turnkey contractor’s staff while training the main body of the national staff, with a subsequent formal handover to the operating organization after a period of one to three years; | ||
| + | *A mixture of experienced and newly trained staff in appropriate positions (e.g. for early Chinese NPPs, approximately one-third of the staff were taken from other plants, one-third from research reactors and one-third from their ‘nuclear’ university). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Post-phase 3 (operations, decommissioning)==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The completion of commissioning of the NPP marks the beginning of what should be, by current norms, a | ||
| + | 40–60 year operating phase, followed eventually by decommissioning. Throughout this period of operations, | ||
| + | specialist support (including research and development) will be needed for a variety of activities, for example: | ||
| + | *Periodic routine maintenance; | ||
| + | *In-service inspection (ISI) and other non-destructive testing (NDT) activities; | ||
| + | *Refurbishment/replacement of obsolete systems/components; | ||
| + | *Upgrading of reactor/turbine power output; | ||
| + | *Development of the case and implementation of the necessary enhancements to extend the operating life of the plant (life extension). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The same can also be said for the decommissioning phase of the NPP. While the vendor and/or other specialist | ||
| + | external contractors already exist to provide such support, and the timescales for the development of such national | ||
| + | capability are longer, decisions need to be taken at an early stage concerning the extent of desired national | ||
| + | involvement in these activities in order to build any requirements into the national workforce plan and contract | ||
| + | tender requirements as appropriate. Some aspects of this are discussed in more detail in the next section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Steps for workforce planning=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is recommended that the following activities related to workforce planning be implemented when getting | ||
| + | started (for Phases 1 and 2): | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Produce a brief (1 or 2 page) conceptual statement on human resources development for the nuclear programme (to be developed during Phase 1 in support of a ‘road map’ for the nuclear power programme). | ||
| + | # Develop a human resources development strategy for the entire nuclear programme that considers all of the areas identified in Fig. 1 to be included in the feasibility study (which is the principal output of Phase 1). | ||
| + | # Develop a workforce plan for all activities to be conducted during Phase 1 and for those expected to be performed in Phases 2 and 3 if a decision is made to go forward with the programme. This plan should be continually updated as the project goes forward. | ||
| + | # Based on the outputs of 2 and 3 above, identify the requirements for NPP personnel selection, recruitment, training and authorization for which assistance is to be sought from the vendor (to be developed during Phase 2 as an input to the bid invitation specification). | ||
| + | |||
| + | A project approach should be taken to develop the above outputs driven by a suitable project manager. When | ||
| + | a NEPIO has been established, one of the members of the NEPIO should be assigned for managing/coordinating | ||
| + | human resources development activities. | ||
| + | The initial workforce plan may be efficiently developed in the following manner: | ||
| + | * Start with a self-evaluation of infrastructure status [4]; | ||
| + | *Identify gaps for all 19 issues, phase by phase, based on organizational responsibilities and activities; | ||
| + | *Identify underlying causes, including lack of competent personnel; | ||
| + | *Define solutions, including human resources related solutions in terms of numbers of people needed,organizations, competencies; | ||
| + | *Implement solutions; | ||
| + | *Evaluate effectiveness of actions/solutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Source:''' [[Workforce Planning for New Nuclear Power Programmes]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, The Management System for Facilities and Activities, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-R-3, IAEA, Vienna (2006). INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY Agency, Workforce Planning For New Nuclear Power Programmes, Nuclear Energy Series, No. NG-T-6.2, IAEA, Vienna (2011). |
| + | |||
| + | [2] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Milestones in the Development of a National Infrastructure for Nuclear | ||
| + | Power, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-G-3.1, IAEA, Vienna (2007). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [3] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Responsibilities and Capabilities of a Nuclear Energy Programme | ||
| + | Implementing Organization, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-3.6, IAEA, Vienna (2009). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [4] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Initiating Nuclear Power Programmes: Responsibilities and Capabilities of | ||
| + | Owners and Operators, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-3.1, IAEA, Vienna (2009). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [5] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Manpower Development for Nuclear Power: A Guidebook, Technical | ||
| + | Reports Series No. 200, IAEA, Vienna (1980). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [6] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities, | ||
| + | IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-G-1.1, IAEA, Vienna (2002). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [7] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Training the Staff of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities: A | ||
| + | Competency Framework, IAEA-TECDOC-1254, IAEA, Vienna (2001). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [8] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource | ||
| + | Considerations, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-2.2, IAEA, Vienna (2008). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [9] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Recruitment, Qualification and Training of Personnel for Nuclear Power | ||
| + | Plants, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. NS-G-2.8, IAEA, Vienna (2002). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [10] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Nuclear Power Plant Personnel Training and Its Evaluation: A Guidebook, | ||
| + | Technical Reports Series No. 380, IAEA, Vienna (1996). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [11] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Nuclear Power Plant Organization and Staffing for Improved Performance: | ||
| + | Lessons Learned, IAEA-TECDOC-1052, IAEA, Vienna (1998). | ||
| + | |||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
| + | [[Capacity building]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Succession planning]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Human resource management]] | [[Human resource management]] | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Educational programme]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Human resource management]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:45, 21 December 2015
Contents
- 1 Definition
- 2 Summary
- 3 Workforce Development Approach
- 4 Workforce Planning For New Nuclear Power Programmes
- 5 References
- 6 Related articles
Definition
The process that identifies or anticipates vacant positions and the required staffing levels and skills to ensure the retention of institutional knowledge and critical skills and competences to support future business strategies
Summary
The IAEA estimates future nuclear electricity generating capacity in the world. The number of operating nuclear reactors is projected to increase by about 90 by 2030 from the total of 437 reactors at the end of 2013. The purpose of this article is to provide member states and organizations with methodology to understand the role of Workforce Planning for ensuring safe, reliable and efficient nuclear facility operations. For a country that does not already have nuclear power, and even for those wishing to significantly expand an existing nuclear energy capability, it may take up to 10–15 years to develop the necessary infrastructure. This article will provide knowledge how the essential elements of a Workforce Planning Program for existing and new NPP's.
Workforce Development Approach
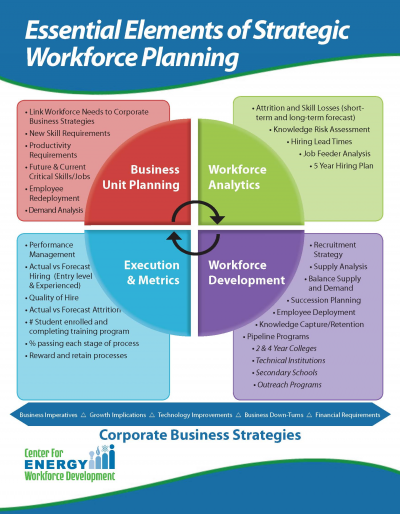
Strategic approach for workforce development means systematic process of interconnection between economic and safety goals of NPP with organizational knowledge asset which is provided by sufficient qualified workforce.
Many nuclear organizations recognize that a strategic approach is most effective in addressing the broad array of workforce issues, which many organizations face. While this publication focuses on managing the risk associated with potential loss of nuclear knowledge, the interactions between KM and other HR development programmes should be considered. These programmes may include the following:
- Workforce planning;
- Recruiting initiatives;
- Talent acquisition initiatives;
- Training programmes;
- Succession planning and leadership development;
- Knowledge management;
- Organizational competency management
The concept of strategic approach for workforce development is shown on Figure 1.
Knowledge loss risk management as a process of KM find its place in the context of workforce development as a systematic process for identifying gaps in organizational competency due to potential staff attrition. After evaluation of the knowledge loss threats, action plan should be developed to mitigate the risks. For example, if a potential for knowledge loss is identified involving a plant expert, solutions may involve a recruiting initiative and/or developing a formal training module. The pending retirement of an experienced component engineer may require recruiting, training, and succession planning. There are numerous other examples where an integrated, strategic approach is taken to ensure the overall effectiveness of nuclear programmes. More detail HR workforce planning approach is in IAEA publication [1]
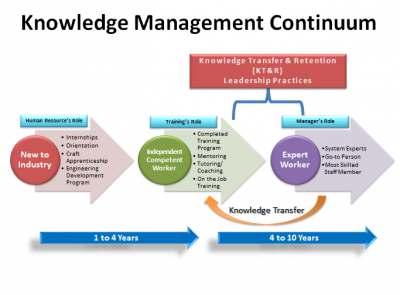
As part of workforce planning, knowledge transfer and retention begins at the time of hire and moves through the employee life-cycle. General life-cycle of knowledge transfer for the nuclear specialist is shown on a Figure 2. Newly hired employees complete required initial training for their positions as part of new-hire orientation and assimilation. Many positions require certification and/or qualifications through extensive, formalized training programmes. Upon completion of those programmes, employees qualified to perform their tasks are considered ‘independent’ workers. These individuals are capable of performing their jobs; however, they may not be as proficient as an expert, long-term employee. Through the effective use of knowledge management, managers can accelerate a newer employee’s technical capabilities and can help transfer critical/unique knowledge. Important role in workforce development plays KM culture. Establishment of motivation mechanisms to encourage highly qualified staff to share knowledge and skills are very important for the reason that knowledge sharing culture supports safety culture.
Workforce Planning For New Nuclear Power Programmes
Analysis of infrastructure activities, competencies and resource requirements
As indicated earlier, a prerequisite for developing a workforce plan to support a national nuclear power programme is to clearly define in Phase 1 (considering the feasibility of nuclear power for the country) the roles, responsibilities and functions of all the stakeholder organizations to be involved. As the programme progresses into Phase 2, this is likely to include, as a minimum, the NEPIO, an independent regulatory body and a designated operating organization. The workforce planning process can then be used to identify the major activities that need to be undertaken to achieve the milestones, which organizations should be responsible for these activities, and the competencies needed. A part of this process will be to determine which of these activities are within the current national capability, which could be undertaken nationally in the longer term (with training and support) and which should be contracted out from the outset.
In addition to the nuclear related activities of a nuclear energy programme, as with all major capital projects, significant non-nuclear resources will be needed, particularly in the early construction stages of the programme. For general guidance on workforce development for the implementation of a nuclear energy programme, Member States may find the IAEA publication on Manpower Development for Nuclear Power: A Guidebook [9] useful. Although this publication, issued in 1980, was based on the previous generation of nuclear energy programmes, much of the content is still relevant. For more detailed workforce planning, the main IAEA publications providing useful guidance are listed in Table 6 at the end of this section, indicating those organizations and the phases to which they are most applicable.
The workforce planning process for a specific nuclear energy programme should begin with a review of the activities identified under each of the 19 infrastructure issues, phase by phase (as identified in Ref. [1]), which should form the basis for an initial analysis of competence and resource needs. It is important to remember, however, that although the infrastructure issues have been separated into 19 discrete topics, in reality the activities associated with these topics are often integrated and interdependent. The same individuals may be engaged in various activities covering several infrastructure issues. Hence, for workforce planning purposes, it is more appropriate to consider these activities in terms of organizational responsibilities. In some cases, it is clear where responsibilities should be assigned for particular activities; in others, it will be a judgement based on the particular national organizational arrangements.
During Phase 1, the NEPIO is likely be the major responsible organization and, in addition to the information contained in the Milestones publication, an overview of its functions and responsibilities during Phase 1 is provided in Table 2, taken from Ref. [2].
During Phase 2, the regulatory body and operating organization will be assigned (assuming they were not already assigned in Phase 1), and responsibilities, and therefore resource requirements, will progressively be transferred to these organizations. Table 3 [2] provides an overview of the NEPIO’s functions and responsibilities during Phase 2, and a similar overview of the responsibilities of the operating organization during Phase 2 is included in Table 4 (taken from Ref. [3]). Useful sources when developing workforce plans for the regulatory body include Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities [10] and Training the Staff of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities: A Competency Framework [11].
From the beginning of Phase 3, the major workforce planning effort is likely to be focused on the operating organization in order to adequately resource, first, the commissioning and, subsequently, the operation of the NPP. Table 5 provides a summary of the responsibilities of the operating organization during Phase 3. The IAEA publication Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource Considerations [12] contains guidance for planning purposes. Inputs for workforce planning for the organizational and resourcing requirements of the operating organization to actually operate the plant, will depend, to some extent, on the design of the NPP selected. It is likely that the vendor of the chosen design will have recommendations in this area. Member States may find broader guidance on the recruitment, training and qualification of these staff in Refs [13, 14].
TABLES 1-6 not Wikified.
Prerequisites for workforce planning (Phase 1)
As stated previously, a prerequisite for effective workforce planning for a nuclear power programme is the establishment of clear roles, responsibilities and functions for all of the organizations that will have a role in considering a nuclear power programme. Absent these roles, responsibilities and functions, there is no framework/basis for workforce planning. The establishment of a NEPIO as described in Ref. [2] is one way in which to effectively develop these roles, responsibilities and functions, as well as to foster coordination among those organizations involved in considering a nuclear power programme. However, these roles, responsibilities and functions can certainly be determined without having a NEPIO in place.
Developing a workforce plan
Summarizing the foregoing, for every country developing a nuclear energy programme, the workforce plans will be different, based on factors such as:
- Scope (and main purpose) of the construction build programme;
- Nature of construction build programme (fully turnkey versus transition to indigenous construction) and subsequent relationship with the vendor;
- Availability of nuclear expertise from non-energy applications (industry, medical, agriculture, applied sciences);
- Access to available international nuclear expertise;
- Existing (if any) nuclear educational programmes;
- Availability and quality of non-nuclear workforce.
The quantity and variety of resources needed to establish a nuclear energy programme can be phased in over the development of the programme and can begin with quite small numbers. For example, the owner/operator project team needed to manage the specification and contracting of the first NPP during Phase 2 may be as few as 30–35 personnel (assuming a turnkey project where the supplier has overall responsibility for management of construction and commissioning).
Overview
Workforce planning is an essential, ongoing human resources management process. Each organization involved in the nuclear energy programme should develop and maintain its own workforce plan; at least for Phases 1 and 2, the NEPIO should maintain an overall plan to enable an integrated national approach to resource utilization and development. In developing the national workforce plan, it is important to gain an understanding of how the workflow, and therefore the required resources and associated competencies, evolve as the programme develops:
- During Phase 1, the NEPIO will be responsible for most of the activities being undertaken. The number of staff involved will be relatively small and individuals may be drawn from various government departments, with much of the actual specialist work being done by external experts/expert groups. The work to be undertaken during Phase 1 will range from the development of recommendations concerning national policy in some areas through to more detailed analysis in others. Thus, some staff will be working at quite a high level, while others will be involved in more detailed activities (as stated earlier, Ref. [2] deals with the establishment and specific responsibilities of the NEPIO).
- At the beginning of Phase 2, the NEPIO will still be driving the programme, but the other key responsible organizations, including the regulatory body and the owner/operating organization, should be fully established and taking an increasingly active role. The core project team for the construction of the plant should be in place, as even at this early stage there will be a wide variety of activities to be managed, and early recruitment of those operations staff with long training lead times (see Section 5.4) should be under way.
Towards the end of Phase 2, the NEPIO should have handed over many of its early responsibilities to the various responsible organizations and may indeed be considered to have completed its responsibilities.
- By the beginning of Phase 3, although the NEPIO may still have an oversight/coordination role, especially if the first NPP is part of a bigger programme, primary responsibility for management of NPP construction and commissioning should be with the operating organization. The regulatory body will be actively engaged in the licensing of the site and plant design as well as overseeing manufacturing and construction, as appropriate. The operating organization will be actively recruiting and managing the training of its permanent plant staff.
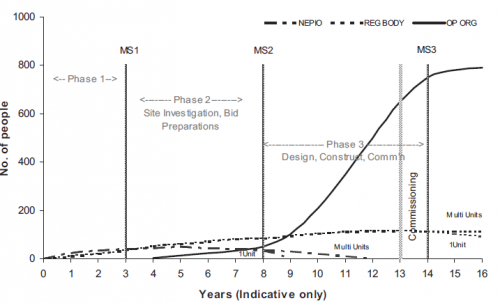
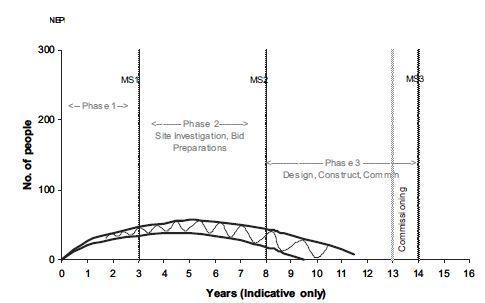
This profile of resource requirements is illustrated in Fig. 3. From an education/qualification perspective, during Phases 1 and 2 of infrastructure development, the majority of the core staff needed will be at the professional/graduate level. However, when staffing the NPP for the operations phase, the graduate component is generally the minority part of the total workforce, with the majority of the workforce being ‘technician’ level staff (i.e. staff who may only have high school level educational qualifications, coupled with some form of vocational skill certification and/or apprenticeship. These staff will require less ‘nuclear’ knowledge than their graduate counterparts but will need considerable training in order to understand the quality and safety requirements of working in a nuclear environment and why nuclear is different from other engineering and industrial environments.
Recruitment considerations
Considerations for staffing a nuclear energy programme
Overall approach
National recruitment processes and practices vary from country to country and may have a significant impact on the workforce planning process. However, nuclear energy programmes require staff of the highest calibre, and it is common practice for educational and/or qualification/licensing requirements to specified by the regulatory body, at least for certain safety related roles. It may therefore be necessary to implement a specific process for the recruitment of staff. Depending on the national education capability, some organizations are able to recruit their professional talent directly at the graduate level by a competitive process that may result in several hundred candidates applying for one or more jobs. This then requires screening to select perhaps 6–10 candidates for interview, which is a time consuming and resource intensive process. At the other extreme, some countries establish nuclear ‘academies’ or universities and select students directly from secondary education with the expectation that the vast majority of ‘graduates’ from these establishments will be employed directly by the industry, thereby simplifying the ‘recruitment’ process.
It is good practice to set limits on the duration of the recruitment process, from the announcement of a job opportunity to the day of appointment. This might be days or months, depending on whether the job is at a support staff or professional level, but it sets expectations on the part of both the recruiting organization and the applicants.
Another important consideration related to the duration of the recruitment process is the scope and duration of any job related training considered necessary prior to an individual’s being authorized to undertake his or her allocated duties. This may range from a few weeks of familiarization for an experienced technical specialist working narrowly within his or her field to several years for a plant operator who may only have secondary education level qualifications.
Hence, for some positions (e.g. operations, reactor engineering, radiological safety and training), it will be necessary to begin the recruitment process several years prior to the individual’s being needed to undertake his or her duties, even prior to signing the contract for the plant.
In an area where several Member States are considering implementing a nuclear energy programme, one practical approach might be to establish a regional training centre (RTC), thus sharing the burden as well as the benefits of specialist nuclear training among several Member States. There are a number of potential benefits in developing an RTC, including:
- Set-up as well as running costs are shared between several Member States.
- An RTC avoids competition between individual Member States in trying to attract scarce specialist resources to provide nuclear training.
- RTCs are more likely to attract the support of international organizations, such as the IAEA, and are more likely to be able to establish links/partnerships with other international training/educational institutions, operating organizations and suppliers.
- Member States may be less likely to lose staff to neighbouring countries if the whole region has adequate access to such specialist training resources.
Such RTCs where staff can receive training would be particularly beneficial during the early phases of a nuclear energy programme, before there is an operating NPP or even an NPP construction project.
An essential element of developing competence is the need to gain practical training and experience. Some elements of this are discussed in the next section, but, inevitably, it will be necessary to find a means of placing some personnel within existing nuclear operating organizations. The existence of an RTC and the possibility of such a facility establishing international links may also be of benefit in this respect.
Phase 1
The initial resourcing of Phase 1 presents a major challenge in workforce planning, as a Member State is unlikely to have all or even many of the needed competencies, particularly those relating to nuclear power. Even starting with a zero baseline, the staff required for Phase 2 will have had the opportunity to develop their initial competence during Phase 1, and similarly for Phase 3. Hence, building competence during Phase 1 is vital for the success of the subsequent phases. An essential component of building that competence is giving staff real experience at the earliest possible opportunity.
One way of providing staff with the opportunity to gain experience during Phase 1 is to adopt a combined approach of importing international expertise to support the overall programme, while at the same time placing national staff overseas to gain experience. This approach may usefully be adopted by all responsible organizations: the NEPIO, regulatory body, operating organization, national industrial organizations hoping to participate in the manufacturing and/or construction of the plant, academic institutions involved in the development of national capability in the medium to long term, and those scientific/research and technical support organizations which may provide services to the plant throughout its life cycle.
External expertise has been successfully used in a number of different ways, for example:
- Contracting out whole work packages to experienced consultants, but including requirements to utilize/train national staff in delivering the work package (where little or no national competence exists in the particular area);
- Contracting with consultants to become ‘temporary’ staff working with nationals to deliver work packages, adding value in the more complex areas while developing national staff (where a modest level of competence exists);
- Engaging senior consultants to ‘coach’ national staff in specific areas of competence (where a higher level of national capability exists);
- Organizing national conferences/workshops where vendors and specialist support organizations can present their capabilities and services (care needs to be taken to ensure that no suggestion of preference or commitment to future business is implied).
Similarly, there are a variety of ways in which staff can be given the opportunity to build competence and experience overseas:
- Establishing bilateral and multilateral relationships with governments, regulatory agencies, vendors, utilities, educational institutions and others, which allow for placements and staff ‘swapping’;
- IAEA training courses, fellowships and internships;
- Formal courses of overseas study (e.g. vocational, undergraduate and postgraduate programmes, which may include industry assignments) and training (directly with utilities/national nuclear training organizations);
- Building staff training and development assignments into potential contracts with vendors, consultants, service providers, etc.;
- Developing ‘strategic alliances’ with vendors/equipment suppliers whereby national organizations obtain licenses to manufacture components in-country, which can include training and qualification in the country of origin.
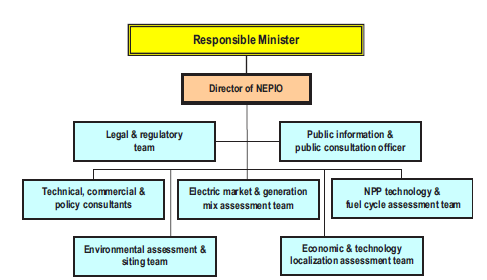
Fortunately, the number of staff directly involved in Phase 1 is relatively small, maybe only 20–30 people, although this number would require the additional support of expert groups, either nationally or internationally. Most, if not all, of these staff will be within the NEPIO, and these staff are likely to be heavily supported by national/international expertise. An example of how this group might be organized is illustrated in Fig. 4.
If a Member State has an existing regulatory body for non-energy applications, this group can be used to undertake the initial work relating to the establishment/revision of legal and regulatory requirements for nuclear energy during Phase 1, even if a separate regulatory body for nuclear energy is to be established in due course.
While it may be difficult to make any long term staffing decisions prior to a formal decision on whether to proceed with a nuclear energy programme at Milestone 1, due to the constraints of the recruitment and training requirements described above, consideration should be given to commencing recruitment of some key staff during Phase 1, to be available for work in Phase 2.
Phase 2
This will be a very busy and diverse period in terms of workforce planning and staff recruitment, and so it is easier to address each of the three main groupings separately.
Nepio
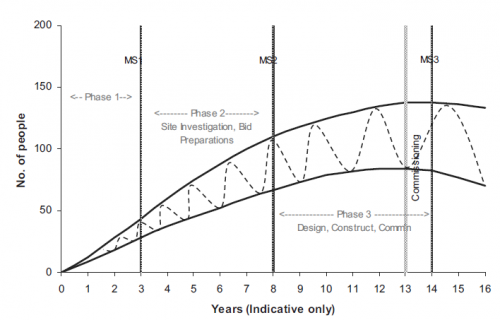
The staffing of the NEPIO will peak during this phase, as can be seen in Fig. 5, typically in the range on 20–50 staff members, depending of the level of specialist support available. By the end of Phase 2, many of their responsibilities should have been transferred to the other responsible organizations, especially the regulatory body and the operating organization. Depending on the size of the nuclear energy programme, the NEPIO may cease to exist as such (or its role may shift to one of purely coordination), with some of its oversight responsibilities (and resources) being transferred to the appropriate regulatory agencies and others being placed within those government departments which would normally be responsible for such activities. In addition, based on the experience they have gained, key NEPIO staff may be transferred into senior positions in the operating organization, either within the nuclear plant management structure (single NPP) or in the corporate organization (multi-unit programme). It is important however that, even if the NEPIO ceases to exist as an organization, the government continues to demonstrate its commitment to, and support for, the nuclear energy programme, and that key individuals within the appropriate government departments have the authority and responsibility to continue promoting the programme.
Regulatory body
The development of the work processes, human resources and competencies of the independent regulatory body is a high priority task in Phase 2 and will continue through Phase 3. During Phase 2, the regulatory body will be proposing and promulgating safety regulations and guides, as well as adopting appropriate industrial codes to properly cover all foreseen nuclear activities.
The number of staff of the regulatory body will depend on two key factors:
- The number of organizations available to provide technical support to the regulatory body (Section 2.2);
- The regulatory approach adopted by the Member State (Section 2.4).
Typically, the regulatory body may have a core staff of about 40–60 people with the competencies to develop or adopt safety regulations, develop and implement an authorization process, review and assess the safety and design documentation provided by the operating organization against the adopted regulations, and inspect the facility, the vendor and manufacturers of safety related components.
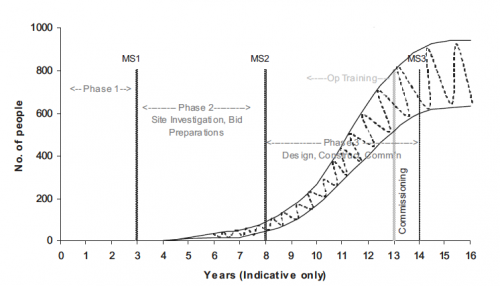
Peak numbers within the regulatory body may be higher, for example, up to 100–150 personnel, again dependent on the level of specialist independent support available and on the number of NPPs planned (workload). In the case of only one plant, these numbers should decline over commissioning, as illustrated in Fig. 6.
It is generally accepted that regulatory bodies should have competencies in four main areas:
- Legal basis and regulatory processes;
- Technical disciplines;
- Regulatory practices;
- Personal and interpersonal competencies.
Detailed guidance on the development of these competencies for regulatory body staff may be found in Ref. [11], and the IAEA can provide assistance in this area.
Operating organisation
Purely from an operational point of view, the planning and recruitment of the staff that will eventually operate the plant needs careful consideration at an early stage in the programme for the following reasons:
- The number of staff required is much larger than for the other organizations, typically in the range of 500–1000 for a single or twin unit plant, up to several thousand for a multiple unit plant (see Section 5.4).
- Many of the operating organization staff have safety related roles as described above, requiring authorization, and hence have significant training programmes, required up to several years for completion (much of such training may be initially conducted at reference plant(s) overseas).
- The commissioning of an NPP, especially if it is a country’s first plant, presents a unique opportunity for staff to gain practical experience. For those staff with specific responsibilities during the commissioning phase, their initial training must be completed. For other staff who do not have specific responsibilities, the commissioning phase still provides opportunities to observe activities and gain practical experience. For these
staff to gain maximum benefit and to avoid resource conflict, at least initial classroom training should be completed prior to the main commissioning phase. The IAEA publication Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource Considerations [12] provides guidance in this area.
In addition, for a first NPP, there are many other activities to be carried out by the future operating organization, such as:
- Preparing the BIS;
- Preparing the environmental impact assessment report (EIAR);
- Establishing interfaces with the various national and international bodies associated with safeguards, security, physical protection, the nuclear fuel cycle and radioactive waste;
- Establishing the integrated management system needed to ensure the safe operation of the plant;
- Creating the foundations of an appropriate safety culture prior to commencing construction;
- Preparing a strategy for dealing with the public;
- Starting to prepare emergency plans and procedures;
- Other (see Ref. [3]).
In order to ensure that there are enough competent staff available for these activities, it will be necessary to begin the recruitment and training of operating organization staff early in Phase 2 (see Fig. 7).
Phase 3
By the beginning of Phase 3, the majority of NEPIO staff is likely to have either transferred to one of the other responsible organizations or returned to one of the government departments with ongoing responsibility for the nuclear energy programme. The majority of regulatory body staff should be in place, undertaking training and discharging their responsibilities in respect of the licensing process.
A project team should be established within the operating organization and fully staffed and competent to meet its responsibilities. This team will oversee the project on behalf of the Member State/operating organization, as distinct from the vendor established project management team (PMT), which will manage the actual construction of the NPP and which may include representatives of the operating organization [3]. It is recommended that this team is part of the operating organization in order to retain their experience and expertise, although different practices may be found in different countries. This also depends on the size of the nuclear energy programme. A key issue here is to ensure that senior PMT staff are not also designated to be senior plant operations staff, as their project management responsibilities during commissioning are likely to conflict with the opportunities for operations staff to gain unique hands-on experience during the commissioning phase.
Plant staff
During this phase, the majority of the plant operating staff, especially technical staff, should be recruited and fully trained. In reality, the actual staff numbers required will vary from plant to plant. This is even true in Member States currently operating many NPPs. This can be for a variety of reasons, including:
- Stand-alone NPP or part of a fleet of NPPs with one operating organization and entralized support functions;
- Regulatory requirements specified by the Member State’s national nuclear regulator;
- Regulatory requirements specified within the Member State by provincial regulators;
- Minor differences in design, even on twin/multi-unit sites;
- Concept of operations, including the level of plant automation and control, and approach to maintenance (in-house staff, joint maintenance by operating utility staff or external contractors);
- Physical attributes of the NPP — physical layout of plant systems/equipment;
- Local labour conditions;
- National/local laws/regulations on labour and employment practices;
- Support relationships with vendors/suppliers.
To give readers of this publication a better understanding of the staffing needed by the end of Phase 3 for the operating organization (the largest of the nuclear organizations to be established), Appendix I provides an example of the median staffing levels by function for some 67 one-unit and two-unit NPPs in operation in North America and western Europe (see notes in the appendix), giving totals of approximately 700 for a single unit plant and 1000 for a twin unit. A description of each of the functions is included in Appendix II for clarity. It must be emphasized that these figures are presented as examples only, as actual numbers will depend on many factors, including those listed above.
It should be emphasized that these numbers relate to direct plant staff only. If more than one NPP is to be built, it is likely that a central or ‘headquarters’ function will be established with its own resource requirements, which in turn may impact the numbers required on each unit if some of the functions are centralized (e.g. design authority, technical support, maintenance, finance, procurement). Additional comparative data on staffing numbers can be found in Ref. [15].
The phasing of recruitment of plant staff depends greatly on their training lead times (how long they need for formal training prior to authorization/certification for their duties), and these vary greatly, depending on their roles and responsibilities. Figure 7 provides an example of the phasing of recruitment in years before commissioning, based on the totals given above. An example breakdown of qualification and training requirements (including typical training lead times, based on the stated expected entry-level education requirements) for various functions at a typical US NPP is included in Appendix III. The reader is cautioned that such lead times will vary considerably based upon national norms and regulations regarding factors such as education, vocational training, labour laws and practices, and industry practices. This variability underlines the need for each country to analyse its own situation and needs through its detailed workforce planning.
In terms of staffing a first nuclear plant, a number of options have been used, including:
- Initial operation by a national staff, which is already trained by the vendor but under the supervision of an experienced vendor supplied staff for an initial period;
- An initial period of operation staffed by the turnkey contractor’s staff while training the main body of the national staff, with a subsequent formal handover to the operating organization after a period of one to three years;
- A mixture of experienced and newly trained staff in appropriate positions (e.g. for early Chinese NPPs, approximately one-third of the staff were taken from other plants, one-third from research reactors and one-third from their ‘nuclear’ university).
Post-phase 3 (operations, decommissioning)
The completion of commissioning of the NPP marks the beginning of what should be, by current norms, a 40–60 year operating phase, followed eventually by decommissioning. Throughout this period of operations, specialist support (including research and development) will be needed for a variety of activities, for example:
- Periodic routine maintenance;
- In-service inspection (ISI) and other non-destructive testing (NDT) activities;
- Refurbishment/replacement of obsolete systems/components;
- Upgrading of reactor/turbine power output;
- Development of the case and implementation of the necessary enhancements to extend the operating life of the plant (life extension).
The same can also be said for the decommissioning phase of the NPP. While the vendor and/or other specialist external contractors already exist to provide such support, and the timescales for the development of such national capability are longer, decisions need to be taken at an early stage concerning the extent of desired national involvement in these activities in order to build any requirements into the national workforce plan and contract tender requirements as appropriate. Some aspects of this are discussed in more detail in the next section.
Steps for workforce planning
It is recommended that the following activities related to workforce planning be implemented when getting started (for Phases 1 and 2):
- Produce a brief (1 or 2 page) conceptual statement on human resources development for the nuclear programme (to be developed during Phase 1 in support of a ‘road map’ for the nuclear power programme).
- Develop a human resources development strategy for the entire nuclear programme that considers all of the areas identified in Fig. 1 to be included in the feasibility study (which is the principal output of Phase 1).
- Develop a workforce plan for all activities to be conducted during Phase 1 and for those expected to be performed in Phases 2 and 3 if a decision is made to go forward with the programme. This plan should be continually updated as the project goes forward.
- Based on the outputs of 2 and 3 above, identify the requirements for NPP personnel selection, recruitment, training and authorization for which assistance is to be sought from the vendor (to be developed during Phase 2 as an input to the bid invitation specification).
A project approach should be taken to develop the above outputs driven by a suitable project manager. When a NEPIO has been established, one of the members of the NEPIO should be assigned for managing/coordinating human resources development activities. The initial workforce plan may be efficiently developed in the following manner:
- Start with a self-evaluation of infrastructure status [4];
- Identify gaps for all 19 issues, phase by phase, based on organizational responsibilities and activities;
- Identify underlying causes, including lack of competent personnel;
- Define solutions, including human resources related solutions in terms of numbers of people needed,organizations, competencies;
- Implement solutions;
- Evaluate effectiveness of actions/solutions.
Source: Workforce Planning for New Nuclear Power Programmes
References
[1] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, The Management System for Facilities and Activities, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-R-3, IAEA, Vienna (2006). INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY Agency, Workforce Planning For New Nuclear Power Programmes, Nuclear Energy Series, No. NG-T-6.2, IAEA, Vienna (2011).
[2] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Milestones in the Development of a National Infrastructure for Nuclear Power, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-G-3.1, IAEA, Vienna (2007).
[3] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Responsibilities and Capabilities of a Nuclear Energy Programme Implementing Organization, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-3.6, IAEA, Vienna (2009).
[4] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Initiating Nuclear Power Programmes: Responsibilities and Capabilities of Owners and Operators, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-3.1, IAEA, Vienna (2009).
[5] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Manpower Development for Nuclear Power: A Guidebook, Technical Reports Series No. 200, IAEA, Vienna (1980).
[6] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Organization and Staffing of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. GS-G-1.1, IAEA, Vienna (2002).
[7] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Training the Staff of the Regulatory Body for Nuclear Facilities: A Competency Framework, IAEA-TECDOC-1254, IAEA, Vienna (2001).
[8] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Commissioning of Nuclear Power Plants: Training and Human Resource Considerations, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-2.2, IAEA, Vienna (2008).
[9] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Recruitment, Qualification and Training of Personnel for Nuclear Power Plants, IAEA Safety Standards Series No. NS-G-2.8, IAEA, Vienna (2002).
[10] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Nuclear Power Plant Personnel Training and Its Evaluation: A Guidebook, Technical Reports Series No. 380, IAEA, Vienna (1996).
[11] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Nuclear Power Plant Organization and Staffing for Improved Performance: Lessons Learned, IAEA-TECDOC-1052, IAEA, Vienna (1998).