Difference between revisions of "Asset management"
m |
DavidBeraha (Talk | contribs) (→Definition) |
||
| (60 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | <!-- |
| + | {{Tellervo}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Complete}}, | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Consolidation stage}} | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | |||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
| − | + | {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Description== | |
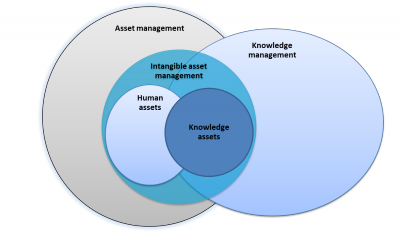
| − | + | [[File:Asset management.png|400px|thumbnail|right|Fig 1 Relationship between asset management related terms.]] | |
| − | Approaches such as the balanced scorecard can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. | + | |
| − | + | Asset management is an approach for the management of a [[Nuclear organization|nuclear organization]] to consider, in a balanced fashion, the entirety of its [[Asset|assets]]. This includes management of tangible assets such as personnel and other animate creatures, facilities, equipment, fiscal investment, inventory, and [[Intangible asset|intangible assets]] such as [[Knowledge|knowledge]], see Fig 1. Asset management involves the balancing of costs, opportunities and risks against the desired performance of assets, to achieve benefits. This balancing might need to be considered over different time frames. Broadly defined, asset management refers to any system that cost-effectively monitors and maintains organization's [[Asset|assets]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Asset management enables an organization to examine the need for, and performance of, assets at different levels. Additionally, it enables the application of analytic approaches towards managing an asset over the different stages of its life cycle (which can start with the conception of the need for the asset, through to its disposal, and includes the managing of any potential post disposal liabilities) [1]. Approaches such as the [[Balanced scorecard|balanced scorecard]] can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. Also a well-planned KM system can contribute to meeting such challenges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===ISO 5000 definition=== | ||
| + | ISO 5000 defines Asset management as the "coordinated activity of an organization to realize value from assets". In turn, Assets are defined as follows: "An asset is an item, thing or entity that has potential or actual value to an organization". This is deliberately wider than physical assets but these form an important focus for more organizations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Institute of Asset Management definition=== | ||
| + | The Institute of Asset Management which is a UK professional body defines Asset Management as "the art and science of making the right decisions and optimising the delivery of value. A common objective is to minimise the whole life cost of assets but there may be other critical factors such as risk or business continuity to be considered objectively in this decision making." [1] | ||
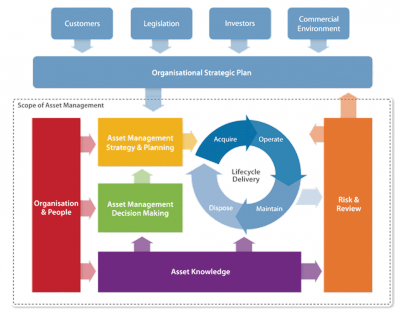
| + | [[File:The institute of asset management asset management conceptual model.png|400px|thumbnail|right|Fig 2 The institute of asset management asset management conceptual model [1]]] Fig 2 depicts the relationship of asset management with other functions. | ||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] The Institute of Asset Management https://theiam.org/what-asset-management |
| + | |||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | [[Asset]] |
| + | |||
| + | [[Intangible asset]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Knowledge asset]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Balanced scorecard]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Asset management]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:35, 21 December 2015
Contents
Definition
Management of organization's assets
Description
Asset management is an approach for the management of a nuclear organization to consider, in a balanced fashion, the entirety of its assets. This includes management of tangible assets such as personnel and other animate creatures, facilities, equipment, fiscal investment, inventory, and intangible assets such as knowledge, see Fig 1. Asset management involves the balancing of costs, opportunities and risks against the desired performance of assets, to achieve benefits. This balancing might need to be considered over different time frames. Broadly defined, asset management refers to any system that cost-effectively monitors and maintains organization's assets.
Asset management enables an organization to examine the need for, and performance of, assets at different levels. Additionally, it enables the application of analytic approaches towards managing an asset over the different stages of its life cycle (which can start with the conception of the need for the asset, through to its disposal, and includes the managing of any potential post disposal liabilities) [1]. Approaches such as the balanced scorecard can be employed to assure appropriately distributed attention to the whole of an organization’s resources. Also a well-planned KM system can contribute to meeting such challenges.
ISO 5000 definition
ISO 5000 defines Asset management as the "coordinated activity of an organization to realize value from assets". In turn, Assets are defined as follows: "An asset is an item, thing or entity that has potential or actual value to an organization". This is deliberately wider than physical assets but these form an important focus for more organizations.
The Institute of Asset Management definition
The Institute of Asset Management which is a UK professional body defines Asset Management as "the art and science of making the right decisions and optimising the delivery of value. A common objective is to minimise the whole life cost of assets but there may be other critical factors such as risk or business continuity to be considered objectively in this decision making." [1]
Fig 2 depicts the relationship of asset management with other functions.References
[1] The Institute of Asset Management https://theiam.org/what-asset-management