Difference between revisions of "Knowledge management strategy"
(→Implementation guide) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
# Business case | # Business case | ||
# Recommended pilots | # Recommended pilots | ||
| − | # Next steps | + | # Next steps |
==Implementation guide== | ==Implementation guide== | ||
| + | Creating a strategy requires interviewing, talking to, and holding workshops with stakeholders from across the organization, as involving the various stakeholder groups ensures that a solution that meets the needs of the organisation is created. Involving stakeholders also helps to understand the current state of KM within the organisation as well as the organisational culture which will be adopting KM. Understanding the culture is a critical part of determining what change management activities will best suit the organization. | ||
| + | The steps to creating the KM strategy are outlined is the diagram to the right: | ||
| + | [[file:KM_Strategy.jpeg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Implementing a KM Strategy after it is created requires time and patience, it is best to take a pilot-based, phased approach and include change management activities throughout the implementation. Taking a pilot-based phased approach means that the roll-out is iterative and adaptive, i.e. agile. This approach allows for adjustments and modifications to the activities and the over-all plan as they come up and avoids the "boil-the-ocean" approach of trying to do everything at once and failing miserably because of lack of resources and understanding of the nuances of the implementation and organisational culture. | ||
==Success factors== | ==Success factors== | ||
Include: | Include: | ||
# Having a strategy | # Having a strategy | ||
| + | # Tying the strategy to the organisation's objectives | ||
# Taking a balanced, integrated approach, i.e. having a KM framework | # Taking a balanced, integrated approach, i.e. having a KM framework | ||
# Making change management integral to the KM implementation | # Making change management integral to the KM implementation | ||
# Senior management buy-in and support | # Senior management buy-in and support | ||
# Implementation is both top-down and bottom-up | # Implementation is both top-down and bottom-up | ||
| + | # Managing the risks | ||
| + | # Having cross-functional involvement | ||
| + | # Having user involvement | ||
==Common pitfalls== | ==Common pitfalls== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 48: | ||
# Not having senior management buy-in and support | # Not having senior management buy-in and support | ||
# Focus either on top-down implementation or bottom-up implementation | # Focus either on top-down implementation or bottom-up implementation | ||
| + | # Ignoring the risks | ||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:22, 9 March 2016
Contents
Definition
A high-level plan to achieve organisational goals with a knowledge management system
Purpose & benefits
The primary purpose for writing a KM strategy is to have an understanding of what is required in order to maximize the benefit to the organization from the resources (time, money, and people) that will be used in implementing KM. Without this understanding the KM program will likely fail.
The benefits of having a strategy include having a roadmap/plan that can be used as a foundation for KM in the organization. It can be used as the basis for agreement and understanding on what will be implemented, it can be used as a cornerstone for the necessary change management that is a critical part of any KM program, it creates the KM framework that ensures that KM is implemented holistically for the organisation, Having a KM strategy helps to secure the budget for the program and understand the current state of KM within the organisation and define the desired future state.
Description
The KM strategy is comprised of:
- Strategic KM principles
- The organizational imperative and focus for KM
- A KM vision for the organization
- Critical knowledge areas
- Stakeholders
- A KM Framework
- Information management
- Change management
- Business case
- Recommended pilots
- Next steps
Implementation guide
Creating a strategy requires interviewing, talking to, and holding workshops with stakeholders from across the organization, as involving the various stakeholder groups ensures that a solution that meets the needs of the organisation is created. Involving stakeholders also helps to understand the current state of KM within the organisation as well as the organisational culture which will be adopting KM. Understanding the culture is a critical part of determining what change management activities will best suit the organization.
The steps to creating the KM strategy are outlined is the diagram to the right:
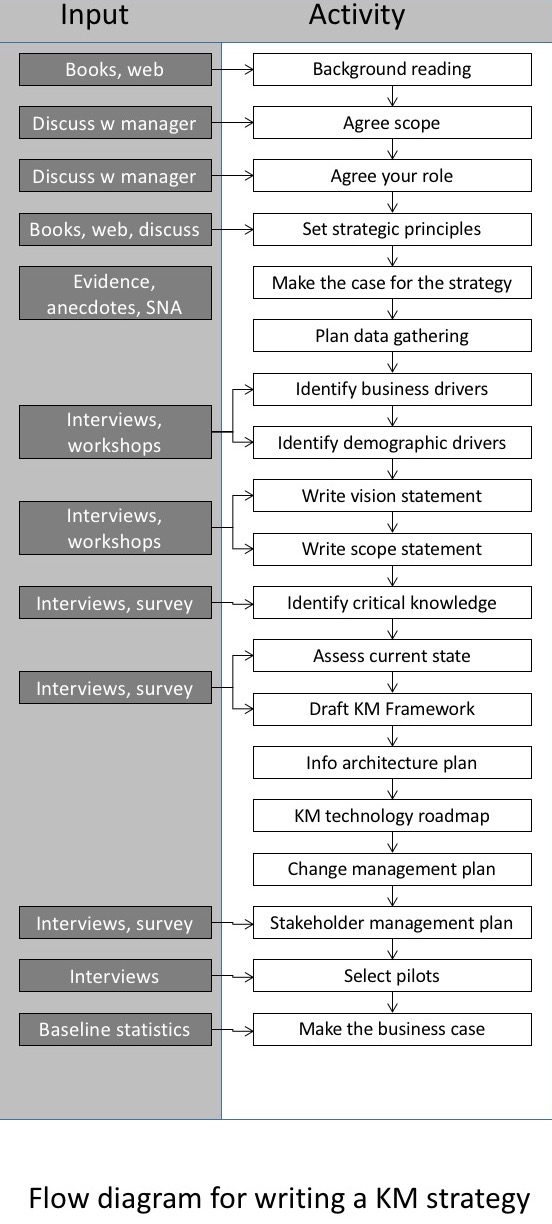
Implementing a KM Strategy after it is created requires time and patience, it is best to take a pilot-based, phased approach and include change management activities throughout the implementation. Taking a pilot-based phased approach means that the roll-out is iterative and adaptive, i.e. agile. This approach allows for adjustments and modifications to the activities and the over-all plan as they come up and avoids the "boil-the-ocean" approach of trying to do everything at once and failing miserably because of lack of resources and understanding of the nuances of the implementation and organisational culture.
Success factors
Include:
- Having a strategy
- Tying the strategy to the organisation's objectives
- Taking a balanced, integrated approach, i.e. having a KM framework
- Making change management integral to the KM implementation
- Senior management buy-in and support
- Implementation is both top-down and bottom-up
- Managing the risks
- Having cross-functional involvement
- Having user involvement
Common pitfalls
Include:
- Trying to implement KM without a strategy, i.e. not creating a KM strategy
- Focusing one aspect of KM, e.g. implementing technology only, or implementing a lessons learned process only
- Not making change management a critical part of the KM implementation
- Not having senior management buy-in and support
- Focus either on top-down implementation or bottom-up implementation
- Ignoring the risks
Related articles
Knowledge management framework
Knowledge management objective