Difference between revisions of "Knowledge model"
From NKM WIKIDOC
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
The models can be classified into three major groups. | The models can be classified into three major groups. | ||
| − | # Component models | + | # Component models: where knowledge is described as being composed of two or more parts |
| − | # Heirarchical models | + | # Heirarchical models: where knowledge can be processed into different types with increasing rarity, value and quality |
| − | # Subjugated models | + | # Subjugated models: where the definition of knowledge is narrowed and described as a subset of something more significant |
| − | + | ||
===Component models=== | ===Component models=== | ||
====Tacit, explicit knowledge model==== | ====Tacit, explicit knowledge model==== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
====Competency,knowledge, skills, attitude knowledge model==== | ====Competency,knowledge, skills, attitude knowledge model==== | ||
[[File:CSKA.png|thumb|right|200px|Fig. 9. Competency,knowledge, skills, attitude knowledge model]] | [[File:CSKA.png|thumb|right|200px|Fig. 9. Competency,knowledge, skills, attitude knowledge model]] | ||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 09:15, 15 November 2013
Template:Comment ,
,
Contents
Definition
Knowledge model is A representation of knowledge used to understand and communicate an aspect of knowledge in the real world.
Summary
A knowledge model describes some aspects of knowledge KM for the purposes of understanding and communication.
Description
There are a number of models which are commonly used in describing knowledge. The models emphasise different elements of knowledge and represent them at different levels of complexity. Some illustrate only the major components of knowledge, others also illustrate systems, subsystems and even processes. This article describes some of those that have been used in IAEA publications in an ascending order of complexity.
The models can be classified into three major groups.
- Component models: where knowledge is described as being composed of two or more parts
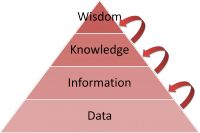
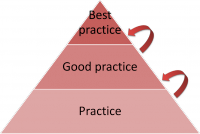
- Heirarchical models: where knowledge can be processed into different types with increasing rarity, value and quality
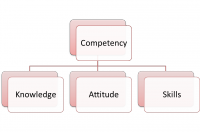
- Subjugated models: where the definition of knowledge is narrowed and described as a subset of something more significant
Component models
Tacit, explicit knowledge model
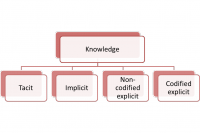
Tacit,implicit,explicit knowledge model
Tacit,implicit,explicit knowledge model
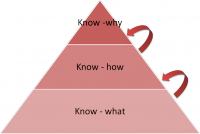
Know-why,know-how,know-what,know-who,know-when,know-where knowledge model
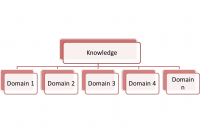
Domains knowledge model
Heirarchical models
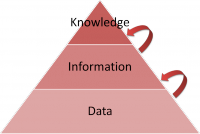
Data, information, knowledge model
Data, information, knowledge, wisdom model
Best practice, good practice, practice knowledge model
Subjugated models
Competency,knowledge, skills, attitude knowledge model
References
[1]