Difference between revisions of "Competency management"
(→Essential components of competency management) |
(→Essential components of competency management) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
On organisation should understand its own organisational capability e.g. by creating and maintaining a human capital index. | On organisation should understand its own organisational capability e.g. by creating and maintaining a human capital index. | ||
| − | On organisation should manage its competency risks. The typical methods for this include creating a map of competency risks at department, business unit, function, organisation levels, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions | + | On organisation should manage its competency risks. The typical methods for this include creating a map of competency risks at department, business unit, function, organisation levels, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions and creating a long-term workforce plan, substitution plan (short term) and a succession plan (long term). |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 11:23, 14 June 2013
Contents
Definition
A collection of processes used to identify and evaluate the current strengths and needs as well as predict the future needs within an organisation and finally to implement the required corrective actions.
Summary
One paragraph
Description
Competency management in the management system
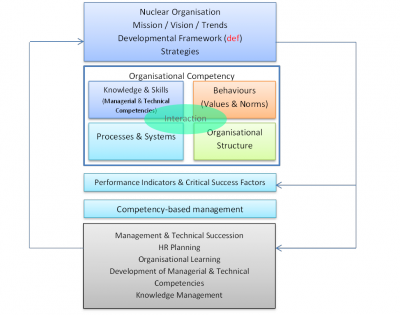
Competency management is a part of a management system. Figure 1 summarises the integration of competency management into a management system.
Figure 1: Organisational Competency interaction
Mission, vision, strategies
Competency management aligns competencies with mission, vision and strategy of the organisation.
Organisational competency
The four elements of organisational competency and their interaction is described in the article on Organisational competency
Performance indicators and critical success factors
Competency based management
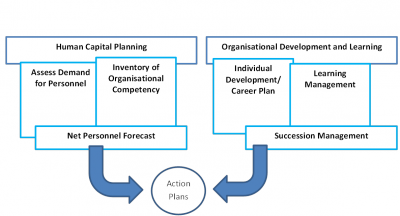
Figure 2 summarises the interface between competency based management and KM.
Figure 2: Competency Based Management – KM Interface
Essential components of competency management
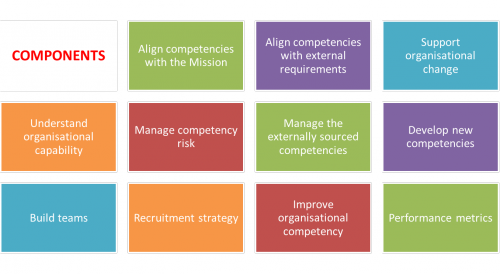
Figure 3 summarises the items an organisation must take care of in order to manage competencies well.
Figure 3: Components of good competency management
Organisational competencies should be aligned with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes of the organisation. The typical methods to acchieve this include creating a scheme of competencies and long-term workforce plan and using the national workforce plan.
Organisational competencies should also be aligened with external requirements and regulations. The typical methods to acchieve this include forming an independent governance and audit committee, integrated quality management system, nuclear safety committee, maintaining and reviewing the minun staffing required for safe operation (Nuclear baseline) and implementing a management of change process.
Competency management should support the process of organsational change or transformation. This includes developing a forward looking business plan, employee development policy, strategy and plan ana a change management plan.
On organisation should understand its own organisational capability e.g. by creating and maintaining a human capital index.
On organisation should manage its competency risks. The typical methods for this include creating a map of competency risks at department, business unit, function, organisation levels, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions and creating a long-term workforce plan, substitution plan (short term) and a succession plan (long term).