Difference between revisions of "Knowledge process"
(→Summary) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
into three primary knowledge processes by which knowledge is [[Production|produced]], [[Validation|validated]] and [[Integration|integrated]] in organizations. | into three primary knowledge processes by which knowledge is [[Production|produced]], [[Validation|validated]] and [[Integration|integrated]] in organizations. | ||
| − | ===[[ | + | ===[[Generation|Knowledge generation]]=== |
*[[Demand|Demand formulation (Internal and external)]] | *[[Demand|Demand formulation (Internal and external)]] | ||
* [[Capture|Capturing]] | * [[Capture|Capturing]] | ||
Revision as of 10:08, 25 September 2013
Contents
Definition
Knowledge process is Knowledge process is a process that acts on /or with knowledge, either individual knowledge or organizational knowledge. Source: [[]]
Summary
knowledge processes includes knowledge generation, validation, maintenance, integration activities with sub processes like acquiring, transforming, developing, disseminating, using, sharing and preserving knowledge as a way to meet specified internal demand that can ultimately improve organizational learning. In this regard, knowledge processes helps an organization to gain insight and understanding from best practices.
Description
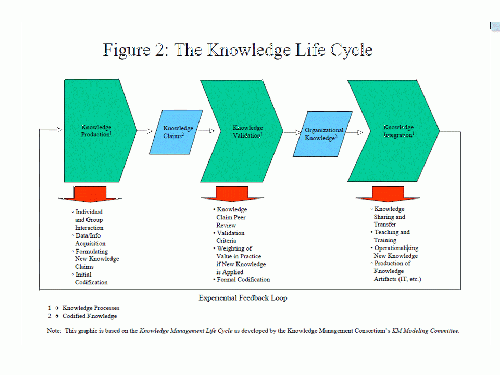
There are many different definitions of knowledge processes used in the literature. Authors such as By Mark W. McElroy [1] describe more widely used and accepted definitions into three primary knowledge processes by which knowledge is produced, validated and integrated in organizations.
Knowledge generation
- Demand formulation (Internal and external)
- Capturing
- Acquisition
- Identification
- Codification
- Creation
- Generation
- Harvesting
- Retrieval
- Learning (individual and group)
Knowledge validation
Knowledge maintaining
Knowledge integration
References
[1] Mark W. McElroy, 2002, The New Knowledge Management - Complexity, Learning, and Sustainable Innovation.