Difference between revisions of "Competency management"
m (198 revisions imported: NKM wiki import 20150315) |
DavidBeraha (Talk | contribs) (→Definition) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
| − | + | {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | |
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
* Align competencies with the mission of the organization | * Align competencies with the mission of the organization | ||
* Align competencies with external requirements ([[Qualification|qualification]]) | * Align competencies with external requirements ([[Qualification|qualification]]) | ||
| − | * Support organisational change ( | + | * Support organisational change (Integrated management system, IMS) |
* Understand organisational capability ([[Organizational competency mapping|gaps and needs assessment]]) | * Understand organisational capability ([[Organizational competency mapping|gaps and needs assessment]]) | ||
* Manage competency risk ([[Organizational competency mapping|gaps and needs assessment]]) | * Manage competency risk ([[Organizational competency mapping|gaps and needs assessment]]) | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Organizational competencies should be '''aligned with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes''' of the organization. The typical methods to acchieve this include creating a scheme of competencies and long-term [[Workforce planning|workforce plan]] based on the mission, vision and strategy and using the national workforce plan. | Organizational competencies should be '''aligned with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes''' of the organization. The typical methods to acchieve this include creating a scheme of competencies and long-term [[Workforce planning|workforce plan]] based on the mission, vision and strategy and using the national workforce plan. | ||
| − | Organizational competencies should also be '''aligened with external requirements and regulations'''. The typical methods to achieve this include forming an independent governance and audit committee, integrated | + | Organizational competencies should also be '''aligened with external requirements and regulations'''. The typical methods to achieve this include forming an independent governance and audit committee, integrated quality management system, nuclear safety committee, maintaining and reviewing the minimum staffing required for safe operation (nuclear baseline) and implementing a management of change process. |
An organization should '''support the processes of organsational change and transformation''' by aligning the competencies with the new requirements. This includes developing a forward looking business plan, employee development policy, strategy and plan and a change management plan. | An organization should '''support the processes of organsational change and transformation''' by aligning the competencies with the new requirements. This includes developing a forward looking business plan, employee development policy, strategy and plan and a change management plan. | ||
| − | An organization should '''understand its own organizational capability''' e.g. by creating and maintaining a | + | An organization should '''understand its own organizational capability''' e.g. by creating and maintaining a human capital index. |
| − | '''Managing competency risks''' is an essential part of competency management. The typical methods to achieve this include creating a map of competency risks at the levels of department, business unit, function or organization, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with [[Retention|knowledge retention]] and [[ | + | '''Managing competency risks''' is an essential part of competency management. The typical methods to achieve this include creating a map of competency risks at the levels of department, business unit, function or organization, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with [[Retention|knowledge retention]] and [[Sharing|transfer]] actions and creating a long-term workforce plan, substitution plan (short term) and a [[Succession planning|succession plan]] (long term). |
| − | An organization should '''manage its externally sources competencies''' which includes maintaining the capability to outsource, ensure that | + | An organization should '''manage its externally sources competencies''' which includes maintaining the capability to outsource, ensure that outsourced capabilities are maintained and managing the risk to outsourced competency. The typical methods to achieve this include developing "Intelligent customer" roles and an outsourcing policy to manage outsourced competency. |
Organization should '''develop its technical and functional competencies'''. The typical methods to achieve this include performing [[Job-task analysis|job-task analysis]], maintaining role and training profiles, having a process for performance assessment and appraisal, analysing learning needs, evaluating the impact of [[Learning|learning]], developing a competency development programme which includes e.g. [[Coaching|coaching]], [[Mentoring|mentoring]], [[Training|training]] and directed reading. | Organization should '''develop its technical and functional competencies'''. The typical methods to achieve this include performing [[Job-task analysis|job-task analysis]], maintaining role and training profiles, having a process for performance assessment and appraisal, analysing learning needs, evaluating the impact of [[Learning|learning]], developing a competency development programme which includes e.g. [[Coaching|coaching]], [[Mentoring|mentoring]], [[Training|training]] and directed reading. | ||
| − | As a part of its competency management, an organization should also '''[[Teamwork|build teams]] and team level competencies'''. The methods for achieving this typically include maintaining and using the organizational structure chart, creating and maintaining, individual and team role and task descriptions, creating and promoting | + | As a part of its competency management, an organization should also '''[[Teamwork|build teams]] and team level competencies'''. The methods for achieving this typically include maintaining and using the organizational structure chart, creating and maintaining, individual and team role and task descriptions, creating and promoting networks and [[Community of practice|communities]] and using the business unit plans. |
'''Developing a recruitment strategy''' supports importing new competencies. The typical methods for acchieving this include developing a [[Recruitment|recruitment]] process and plan and having processes for reassignment, redeployment and job rotation. | '''Developing a recruitment strategy''' supports importing new competencies. The typical methods for acchieving this include developing a [[Recruitment|recruitment]] process and plan and having processes for reassignment, redeployment and job rotation. | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
* Tritaium: SkillsXP (www.tritanium.com); | * Tritaium: SkillsXP (www.tritanium.com); | ||
* Avilar: Web Mentor Skills (www.avilar.com). | * Avilar: Web Mentor Skills (www.avilar.com). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Source:''' | '''Source:''' | ||
[[Knowledge Management for Nuclear Research and Development Organizations]] | [[Knowledge Management for Nuclear Research and Development Organizations]] | ||
| + | ---> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 21 December 2015
Contents
Definition
A collection of processes used to identify and evaluate the current strengths and needs as well as predict the future needs within an organisation and finally to implement the required corrective actions.
Summary
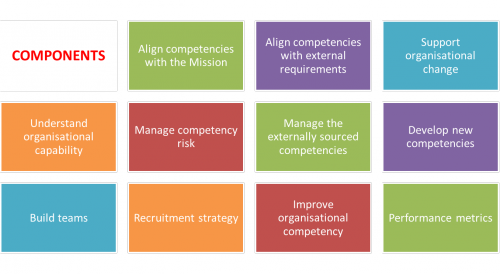
Competency management should be integrated into the management system of the organization. Competency management involves methods for ascertaining both individual and organizational competencies and subsequently connecting them with the main business processes of the organization. Eleven essential components of competency management have been identified for nuclear organizations:
- Align competencies with the mission of the organization
- Align competencies with external requirements (qualification)
- Support organisational change (Integrated management system, IMS)
- Understand organisational capability (gaps and needs assessment)
- Manage competency risk (gaps and needs assessment)
- Manage externally-sourced competencies (qualification)
- Develop new competencies (gaps and needs assessment)
- Build teams (organizational behavior)
- Recruitment strategy (gaps and needs assessment)
- Improve organizational competency
- Performance metrics (KPI's)
Description
Overview
The organization shall
- determine the necessary competence of person(s) doing work under its control that affects its quality performance;
- ensure that these persons are competent on the basis of appropriate education, training, or experience;
- where applicable, take actions to acquire the necessary competence, and evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken;
- retain appropriate documented information as evidence of competence.
- NOTE Applicable actions can include, for example, the provision of training to, the mentoring of, or the reassignment of currently employed persons; or the hiring or contracting of competent persons.
Competency management in the management system
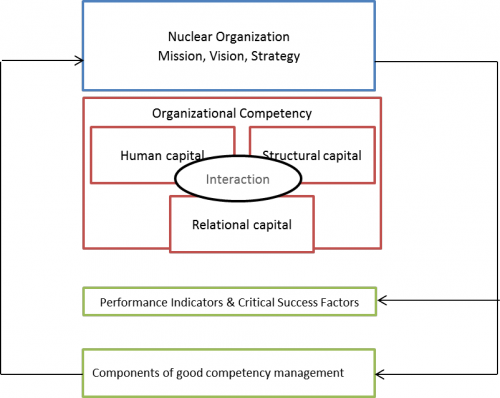
Most nuclear organizations have built a management system which integrates all elements of an organization into one coherent system to enable the organization’s objectives to be achieved. Also competency management should be integrated in this overall management. Fig 1 summarises the integration of competency management into a management system (developed based on [1]).
In order to meet its business objectives, an organization should align its competencies with the mission, vision and strategy. This requires that also the competency management processes and their key performance indicators should be aligned with the overall business objectives.
Essential components of managing organizational competency
Fig 2 summarises the eleven items an organization must take care of in order to manage its competencies well. For discussion on how to construct a competency map which informs the methods for managing the components, see the article on organizational competency mapping
Organizational competencies should be aligned with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes of the organization. The typical methods to acchieve this include creating a scheme of competencies and long-term workforce plan based on the mission, vision and strategy and using the national workforce plan.
Organizational competencies should also be aligened with external requirements and regulations. The typical methods to achieve this include forming an independent governance and audit committee, integrated quality management system, nuclear safety committee, maintaining and reviewing the minimum staffing required for safe operation (nuclear baseline) and implementing a management of change process.
An organization should support the processes of organsational change and transformation by aligning the competencies with the new requirements. This includes developing a forward looking business plan, employee development policy, strategy and plan and a change management plan.
An organization should understand its own organizational capability e.g. by creating and maintaining a human capital index.
Managing competency risks is an essential part of competency management. The typical methods to achieve this include creating a map of competency risks at the levels of department, business unit, function or organization, creating a risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions and creating a long-term workforce plan, substitution plan (short term) and a succession plan (long term).
An organization should manage its externally sources competencies which includes maintaining the capability to outsource, ensure that outsourced capabilities are maintained and managing the risk to outsourced competency. The typical methods to achieve this include developing "Intelligent customer" roles and an outsourcing policy to manage outsourced competency.
Organization should develop its technical and functional competencies. The typical methods to achieve this include performing job-task analysis, maintaining role and training profiles, having a process for performance assessment and appraisal, analysing learning needs, evaluating the impact of learning, developing a competency development programme which includes e.g. coaching, mentoring, training and directed reading.
As a part of its competency management, an organization should also build teams and team level competencies. The methods for achieving this typically include maintaining and using the organizational structure chart, creating and maintaining, individual and team role and task descriptions, creating and promoting networks and communities and using the business unit plans.
Developing a recruitment strategy supports importing new competencies. The typical methods for acchieving this include developing a recruitment process and plan and having processes for reassignment, redeployment and job rotation.
Organizations can also improve their competencies through benchmarking. The typical methods for achieving this include improving job descriptions and role profiles, restructuring posts, processes and systems based on the found good practices.
Developing organizational performance metrics is a way to evaluate the the effect of competencies on performance. The typical methods for achieving this include developing performance assessment and evaluation methodologies.
Management of individual competencies
For nuclear organizations, demonstrating staff competency to regulators and clients in a very important management practice. A related activity is the actual process of maintaining and enhancing competency throughout the entire organization. IT tools are available to help do this. The functionality of most systems available on the market allows:
- The management of personnel data (name, address, job position, qualifications, certifications, experience etc.);
- The construction of competency frameworks;
- Allocation of competencies to roles;
- Competency of individuals to be recorded;
- Training requirements to be allocated and training records maintained;
- Role and task information to be captured;
- Gap analysis reporting
The advantages of implementation of such a system include:
- Means of measuring and thus improving competence in a systematic manner;
- Enables expert competencies to be identified and made available to others in the organization;
- Tangible demonstration of staff competence to clients and regulators, thus assuring regulatory compliance in this area;
- Enables cost effective planning of training across the organization;
- Validity periods for refresher and update training are provided with automatic warnings of expiry;
Competency loss risk assessment
References
[1] S. Gardielliano, Integrative Organizational Competency - A practical and cost-effective model.
Assessment of organizational competency