Difference between revisions of "Organizational competency mapping"
DavidBeraha (Talk | contribs) (→Definition) |
|||
| (119 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Kent}} |
| + | |||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | {{Tidy3}}, | ||
{{Consolidation stage}}, | {{Consolidation stage}}, | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Tellervo}} | ||
{{Priority}}, | {{Priority}}, | ||
| − | + | --> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==Definition== | ==Definition== | ||
| − | + | {{ {{PAGENAME}} }} | |
| − | + | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| − | + | Mapping organizational competency should provide the organization with the information needed for [[Competency management|competency management]]. Thus, it should address the components of competency management and identify the information requirements for constructing the related [[Competency map|competency maps]]. Mapping can be performed on different levels of the organization and in varying levels of detail and thus the details of the approach need to be designed appropriate for the situation in question. The end result, competency map, may also vary in form depending on the selected approach. The competency mapping should support the organization to align its competencies with the strategy and business goals. Thus understanding the context and the essential tasks and functions of the organization is important for a successful mapping process. | |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | === | + | ===Why should organizations map organizational competencies?=== |
| − | + | The purpose of mapping organizational competency is to inform the decisions and actions necessary to [[Competency management|manage organizational competencies]]. It enables an organization to identify its needs and its current stage in order to make an action plan to align competency with mission. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Competency mapping can be done at any organizational level: whole organization, department or team based on priority and importance. The selected mapping technique has to be appropriate, in balance with the effort and return and fit for the purpose and the organization for which it is intended. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Representation of the result - [[Competency map]]=== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | ===Understanding the context of mapping organizational competencies=== |
| + | As the role of competency mapping is to support [[Competency management|competency management]], it is important to understand the context where the mapping is to be performed. Different [[Nuclear organization|nuclear organizations]] have different missions and strategies and different organizational units have different roles in executing the strategy and thus they have different type of core competences. The competency mapping approach needs to be adjusted accordingly. | ||
| − | + | Fig 1 illustrates a framework for considering the possible types of essential [[Organizational competency|organizational competencies]] based on the role of the organization or unit to be mapped. The framework can be used for designing the appropriate mapping approach. It characterizes the possible forms of organizational competency depending on the novelty of the problem solving needed in the organization and on the interdependency of different tasks and roles. This type of quadrant model is a typical approach in KM literature [1,2]. | |
| − | + | [[File:Characterisation-of-competencies.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 1. Characterisation of competencies when designing the mapping approach]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | If the typical tasks of an organization can be specified before-hand or are routine and the tasks and roles are independent of each other (the second quadrant in Fig 1), it is possible to describe the tasks and roles based on pre-described processes. In this case, the organization can be seen as a sum of its individual roles. Here, [[Organizational competency|organizational competency]] is mainly individual competencies applied in the organization’s context and mainly human capital. In an organization with this type of work tasks, the way in which the organization manages and utilises its individual competencies can be one of the areas where competency mapping should focus. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In organizations belonging to the first quadrant of Fig 1, the tasks are routine or can be pre-described, but they require collective effort of several roles. Here the organization is not just the individuals, but also communication and collaboration play a major role. In addition to management of [[Competency|individual competencies]], mapping of [[Organizational competency|organizational competency]] should focus on communication and the collective competencies that enable the required collaboration. This can, for example, be overlapping competencies in different design areas or networks and communities inside and outside the organization. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | From the competency mapping point of view, the lower row of Fig 1 is fundamentally different from the upper row. Here, the tasks of the organization don’t repeat themselves in the same form every time and the organization has to constantly solve novel problems. Although the responsibilities of the organization can be clearly defined, the tasks and problems that the organization has to deal with in order to fulfil these responsibilities are novel and cannot be exactly defined before-hand. Most tasks of [[Technical support organization|TSO’s]], [[Research and development organization|R&D]] and design organizations typically belong to the lower row of Fig 1. In an organization where the roles are mainly independent, the key experts and their competency can be an essential part of the organizational competency and even the organization's strategic core competency. In this case, ways of managing individual competencies and programmes for knowledge transfer can be an important part of the competency mapping. In organizations where the collaboration is needed to complete the tasks, structural capital and informal networks can be an important part of the organizational competency and may need to be in the focus of the competency mapping. | |
===Methods and approaches for mapping competency=== | ===Methods and approaches for mapping competency=== | ||
| − | + | After the organization has studied and understood the context of the mapping process and the areas which, based on its strategy and business goals, are to be the core of the mapping process, it is time to design the process in detail. The following table provides a practical approach based on the elements of [[Competency management|competency management]]. The organization should identify the methods it uses for managing competencies and the information sources for performing the mapping. | |
The following table identifies the essential components of [[Competency management|competency management]] (column1), typical methods of managing each component (column 2) and | The following table identifies the essential components of [[Competency management|competency management]] (column1), typical methods of managing each component (column 2) and | ||
the information required to construct a competency map that informs the method above (column 3). For more discussion on column 1 see the article on [[Competency management|competency management]]. | the information required to construct a competency map that informs the method above (column 3). For more discussion on column 1 see the article on [[Competency management|competency management]]. | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 57: | Line 47: | ||
! Components of good competency management: (What do you need to do in order to manage competence well) !! Typical Methods of managing each component (practical solutions to competency management components) !! Information requirements for constructing the map that informs methods and solutions | ! Components of good competency management: (What do you need to do in order to manage competence well) !! Typical Methods of managing each component (practical solutions to competency management components) !! Information requirements for constructing the map that informs methods and solutions | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Align competencies with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes of the | + | | Align competencies with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes of the Organization. |
|| | || | ||
*Scheme of competencies. | *Scheme of competencies. | ||
| Line 83: | Line 73: | ||
* Can we show we comply? (e.g. records) | * Can we show we comply? (e.g. records) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Support the process of | + | | Support the process of organizational change or transformation. |
|| | || | ||
* Forward looking business plan. | * Forward looking business plan. | ||
| Line 91: | Line 81: | ||
* What is the end state? | * What is the end state? | ||
* What is the difference / gap between where we are now and where we need to be? | * What is the difference / gap between where we are now and where we need to be? | ||
| − | * | + | * What new competencies are required to fill the gap? |
* How can the new competencies be gained ? E.g. make or buy and train or recruit. | * How can the new competencies be gained ? E.g. make or buy and train or recruit. | ||
* Can the individual existing employees adapt or develop new competencies? | * Can the individual existing employees adapt or develop new competencies? | ||
| Line 97: | Line 87: | ||
* Who are the change agents? | * Who are the change agents? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Understand | + | | Understand organizational capability |
|| | || | ||
Human capital index | Human capital index | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * What are the | + | * What are the organization’s demographics? |
* Ages, skills, qualifications, flexibility, mobility, professions? | * Ages, skills, qualifications, flexibility, mobility, professions? | ||
* What are the individual competencies including role-essential and latent competencies and experience profile? | * What are the individual competencies including role-essential and latent competencies and experience profile? | ||
| Line 108: | Line 98: | ||
| Manage competency risk | | Manage competency risk | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * A map of competency risks at department, business unit, function, | + | * A map of competency risks at department, business unit, function, organization levels. |
* A risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions. Long-term workforce plan. | * A risk-based competency retention plan followed up with knowledge retention and transfer actions. Long-term workforce plan. | ||
* Substitution plan (short term). Succession plan (long term). | * Substitution plan (short term). Succession plan (long term). | ||
| Line 148: | Line 138: | ||
| Build teams | | Build teams | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * | + | * Organizational structure chart |
* Individual and team role and task descriptions | * Individual and team role and task descriptions | ||
* Networks and Communities | * Networks and Communities | ||
| Line 170: | Line 160: | ||
* (plus the questions required in the risk management section above) | * (plus the questions required in the risk management section above) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Improve | + | | Improve organizational competency through benchmarking |
|| | || | ||
* Improved job descriptions and role profiles | * Improved job descriptions and role profiles | ||
* Restructured posts, processes, systems | * Restructured posts, processes, systems | ||
|| | || | ||
| − | * What do other | + | * What do other organizations do? |
| − | * What are the benefits to the | + | * What are the benefits to the organization? |
* Why are they structured as they are? | * Why are they structured as they are? | ||
* How did they derive their model? | * How did they derive their model? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Develop | + | |Develop organizational performance metrics |
|| | || | ||
Performance assessment and evaluation methodology | Performance assessment and evaluation methodology | ||
| Line 191: | Line 181: | ||
=== Examples of competency mapping === | === Examples of competency mapping === | ||
| − | + | ====Case study: Competency team builders==== | |
| + | [[File:Case-study-S-Gardelliano.pdf|Case study:Competency team builders and the integrative competency model]] | ||
| − | + | ====Case study: Intelligent customer's capability==== | |
| + | [[File:Case-study-B-Radford.pdf|Case study:Maintaining organizational competency – ‘Intelligent customer’ capability]] | ||
| − | + | ====A hierarchical competency mapping==== | |
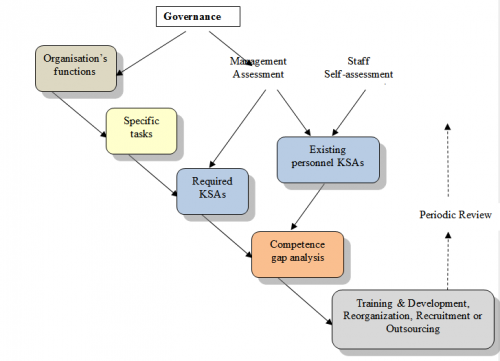
| + | In hierarchical competency mapping, the organization makes an analysis of the functions of the organization, or a part of the organization, and determines the tasks related to those functions. The [[Competency|individual competencies]] (knowledge, skills and attitudes, KSAs) associated with each task are identified and assigned relative weights according to the relevance for a specific task. This process is depicted in Fig 2. | ||
| + | [[File:Use of systematic approach to the analysis of competence gaps.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 2. Use of systematic approach to the analysis of competence gaps]] | ||
| − | + | Competency profiles can be produced to link the function to the required competencies. Competency profiles can also be formed, for example, at a divisional level by combining the required competencies and their weights for the tasks belonging to the function. This process requires the computation of the workload in terms of the number of tasks and the number of times tasks need to be carried out. In addition to a profile of the current needs, a profile for future needs and aspirations of the organization can be established. The assessment of competence needs should be informed by the outcome of the organization’s governance process. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | The | + | The next step of hierarchical competency mapping is to analyse the existing competences of the individual or organizational subdivision in a similar manner to the analysis above and then to carry out gap analysis. A source of information to estimate the existing competency is personal performance reviews as they examine each individual’s competency and discuss proposed competency development. The amount of personnel and competencies which are needed to fill each gap can then be determined. If a critical competence is possessed in only by a single person, the situation should be considered a competency gap. A profile of competency gaps can be produced at any organizational level or for the organization as a whole and the gaps prioritized taking into account their importance to the regulatory functions. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ====Competency mapping based on the role of the organization and the typical work tasks==== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Competency mapping approaches suitable for different work tasks are depicted in Fig 3. If the tasks can be described before-hand and they don’t require much communication (the second quadrant in Fig 3), the existing regulatory requirement, processes and work descriptions are sufficient sources for competency mapping. A hierarchical competency mapping could start from the strategy and business goals of the organization which leads to processes, tasks for groups and roles and finally to competency needs for groups and roles. It is essential for the organization to map which roles are required by which process and what type of individual requirements has to be set for each role. This mapping approach mainly sees organizational competency as a sum of the individual competences and mapping focuses on human capital. This type of mapping approach is described in [3]. | |
| + | [[File:Approaches-for-mapping.PNG|thumb|right|500px|Fig 3. Approaches for mapping]] | ||
| − | + | If the work tasks are routine, but the communication between the roles is essential (the first quadrant in Fig 3), the competency mapping should, in addition to the existing processes, include also analysing the need for communication between the teams and roles. This can include e.g. input/output requirements of the processes, coordination of work tasks or competencies that are needed for collaboration between roles and teams. This mapping approach focuses on human and formal structural capital. | |
| − | + | When the typical tasks of the organization include solving novel problems (the lower row in Fig 3), they cannot be completely pre-described using existing processes and thus the explicitly described processes do not provide a sufficient starting point for mapping of the organizational competency. To maintain and develop competencies in this type of work, constant learning and acquisition of new knowledge is needed. In addition to mapping approaches described in the previous paragraphs, competency mapping that focuses on organizational learning and areas where competencies need to be developed are needed. These mapping approaches start with identifying the expertise areas where novel problems are most likely to occur. After this the current and past success factors and general problem solving approaches are identified. Finally, the organizational learning is addressed. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In organizations where the tasks include novel problems but the roles are mainly independent, (third quadrant in Fig 3) the existing individual competencies can be the basis of some of the organization’s core competencies. In these cases, the organizational competency mapping should also address the human capital imbedded in the individual experts. The mapping should address how the individual competencies are connected to collective competencies and to core competencies and if some individual competencies are critical enablers for upper level competencies. | |
| − | + | In organizations where the tasks include novel problems and require collaboration (fourth quadrant in Fig 3), in addition to individual competencies, also the formal and informal networks are an important part of the organizational competencies. The organizational competency mapping should thus address the enablers of effective problem solving in expert networks and learning processes in these networks. The enablers of networking can be, for example, experts how have wide experience that allows them to collaborate over expertise areas and recognise the areas where collaboration is needed. | |
| − | + | ====Competency loss risk assessment==== | |
| + | =====Mapping competency loss risk===== | ||
| + | Based on the results of [[Competency loss risk assessment|competency loss risk assessment]], managers should develop a strategic plan addressing organizational competence (knowledge) loss and perform corrective actions | ||
| + | Corrective actions mainly can be focused on: | ||
| + | # Determination of prioritized list of competences at risk; | ||
| + | # Critical positions detection; | ||
| + | # Detection of key expert at risk (employees and their critical knowledge and competences); | ||
| + | # Development of substitution plan (reserve) for key employees which are going to leave organization; | ||
| + | # Pairs mentor-successor forming and development of individual plans for knowledge transfer; | ||
| + | # Start of knowledge risk assessment for the critical knowledge identification in accordance with Section 4. | ||
| − | + | <!-- '''Source:''' [[Practical Approaches to Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Organizations]] --> | |
| − | + | =====Competences matrix development===== | |
| + | As a part of [[Competency loss risk assessment|competency loss risk assessment]] nuclear organizations may create competency matrix in compliance with available HR (staff). The matrix shows demand on competences on the rate of one person covers one competence. | ||
| + | Though the practices usually are different, at the same time employee can possess several competences, which are overlapping. This gives nuclear organizations reserve of competences what is very important for successful performance. Managers should take into account all available staff and determine their competences, define which are overlapping. Such approach will provide reflection of current situation, helps to identify competences gaps in specific areas and answered what kind of HR staffing needed for covering them, taking into account new demands. Providing the correction actions on the early stage is proactive response to future risks. | ||
| + | It is important to underline that employees can possess knowledge, skills and experience which cover several organizational competences. | ||
| − | + | <!-- '''Source:''' [[Practical Approaches to Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Organizations]] --> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | [ | + | ==References== |
| + | [1] Bhatt, G.D., Management Strategies for Individual Knowledge and Organizational Knowledge, Journal of Knowledge Management, Vol. 6, Iss. 1., pp. 31-39 (2002). | ||
| − | + | [2] Blackler, F., Knowledge, Knowledge Work and Organizations: An Overview and Interpretation, Organisation Studies, Vol 16, No. 6, pp. 1021-1046, (1995). | |
| − | + | [3] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Industry Organizations, 2006 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
| Line 246: | Line 242: | ||
[[Competency map]] | [[Competency map]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | |
| + | [[Category:Competency mapping]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:51, 21 December 2015
Contents
- 1 Definition
- 2 Summary
- 3 Description
- 3.1 Why should organizations map organizational competencies?
- 3.2 Representation of the result - Competency map
- 3.3 Understanding the context of mapping organizational competencies
- 3.4 Methods and approaches for mapping competency
- 3.5 Examples of competency mapping
- 4 References
- 5 Related articles
Definition
A tool for competency management
Summary
Mapping organizational competency should provide the organization with the information needed for competency management. Thus, it should address the components of competency management and identify the information requirements for constructing the related competency maps. Mapping can be performed on different levels of the organization and in varying levels of detail and thus the details of the approach need to be designed appropriate for the situation in question. The end result, competency map, may also vary in form depending on the selected approach. The competency mapping should support the organization to align its competencies with the strategy and business goals. Thus understanding the context and the essential tasks and functions of the organization is important for a successful mapping process.
Description
Why should organizations map organizational competencies?
The purpose of mapping organizational competency is to inform the decisions and actions necessary to manage organizational competencies. It enables an organization to identify its needs and its current stage in order to make an action plan to align competency with mission.
Competency mapping can be done at any organizational level: whole organization, department or team based on priority and importance. The selected mapping technique has to be appropriate, in balance with the effort and return and fit for the purpose and the organization for which it is intended.
Representation of the result - Competency map
Understanding the context of mapping organizational competencies
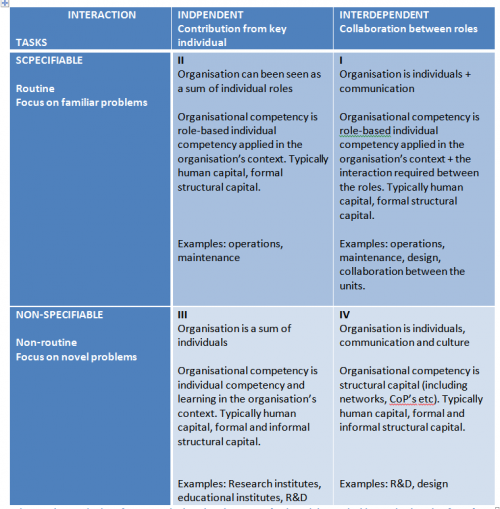
As the role of competency mapping is to support competency management, it is important to understand the context where the mapping is to be performed. Different nuclear organizations have different missions and strategies and different organizational units have different roles in executing the strategy and thus they have different type of core competences. The competency mapping approach needs to be adjusted accordingly.
Fig 1 illustrates a framework for considering the possible types of essential organizational competencies based on the role of the organization or unit to be mapped. The framework can be used for designing the appropriate mapping approach. It characterizes the possible forms of organizational competency depending on the novelty of the problem solving needed in the organization and on the interdependency of different tasks and roles. This type of quadrant model is a typical approach in KM literature [1,2].
If the typical tasks of an organization can be specified before-hand or are routine and the tasks and roles are independent of each other (the second quadrant in Fig 1), it is possible to describe the tasks and roles based on pre-described processes. In this case, the organization can be seen as a sum of its individual roles. Here, organizational competency is mainly individual competencies applied in the organization’s context and mainly human capital. In an organization with this type of work tasks, the way in which the organization manages and utilises its individual competencies can be one of the areas where competency mapping should focus.
In organizations belonging to the first quadrant of Fig 1, the tasks are routine or can be pre-described, but they require collective effort of several roles. Here the organization is not just the individuals, but also communication and collaboration play a major role. In addition to management of individual competencies, mapping of organizational competency should focus on communication and the collective competencies that enable the required collaboration. This can, for example, be overlapping competencies in different design areas or networks and communities inside and outside the organization.
From the competency mapping point of view, the lower row of Fig 1 is fundamentally different from the upper row. Here, the tasks of the organization don’t repeat themselves in the same form every time and the organization has to constantly solve novel problems. Although the responsibilities of the organization can be clearly defined, the tasks and problems that the organization has to deal with in order to fulfil these responsibilities are novel and cannot be exactly defined before-hand. Most tasks of TSO’s, R&D and design organizations typically belong to the lower row of Fig 1. In an organization where the roles are mainly independent, the key experts and their competency can be an essential part of the organizational competency and even the organization's strategic core competency. In this case, ways of managing individual competencies and programmes for knowledge transfer can be an important part of the competency mapping. In organizations where the collaboration is needed to complete the tasks, structural capital and informal networks can be an important part of the organizational competency and may need to be in the focus of the competency mapping.
Methods and approaches for mapping competency
After the organization has studied and understood the context of the mapping process and the areas which, based on its strategy and business goals, are to be the core of the mapping process, it is time to design the process in detail. The following table provides a practical approach based on the elements of competency management. The organization should identify the methods it uses for managing competencies and the information sources for performing the mapping.
The following table identifies the essential components of competency management (column1), typical methods of managing each component (column 2) and the information required to construct a competency map that informs the method above (column 3). For more discussion on column 1 see the article on competency management.
| Components of good competency management: (What do you need to do in order to manage competence well) | Typical Methods of managing each component (practical solutions to competency management components) | Information requirements for constructing the map that informs methods and solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Align competencies with the mission, vision, strategy and business processes of the Organization. |
|
|
| Align competencies with external requirements and regulations |
|
|
| Support the process of organizational change or transformation. |
|
|
| Understand organizational capability |
Human capital index |
|
| Manage competency risk |
|
|
Manage the externally sourced competencies
|
|
|
| Develop management , technical and functional competency |
|
|
| Build teams |
|
|
| Develop a recruitment strategy |
|
|
| Improve organizational competency through benchmarking |
|
|
| Develop organizational performance metrics |
Performance assessment and evaluation methodology |
|
Examples of competency mapping
Case study: Competency team builders
File:Case-study-S-Gardelliano.pdf
Case study: Intelligent customer's capability
A hierarchical competency mapping
In hierarchical competency mapping, the organization makes an analysis of the functions of the organization, or a part of the organization, and determines the tasks related to those functions. The individual competencies (knowledge, skills and attitudes, KSAs) associated with each task are identified and assigned relative weights according to the relevance for a specific task. This process is depicted in Fig 2.
Competency profiles can be produced to link the function to the required competencies. Competency profiles can also be formed, for example, at a divisional level by combining the required competencies and their weights for the tasks belonging to the function. This process requires the computation of the workload in terms of the number of tasks and the number of times tasks need to be carried out. In addition to a profile of the current needs, a profile for future needs and aspirations of the organization can be established. The assessment of competence needs should be informed by the outcome of the organization’s governance process.
The next step of hierarchical competency mapping is to analyse the existing competences of the individual or organizational subdivision in a similar manner to the analysis above and then to carry out gap analysis. A source of information to estimate the existing competency is personal performance reviews as they examine each individual’s competency and discuss proposed competency development. The amount of personnel and competencies which are needed to fill each gap can then be determined. If a critical competence is possessed in only by a single person, the situation should be considered a competency gap. A profile of competency gaps can be produced at any organizational level or for the organization as a whole and the gaps prioritized taking into account their importance to the regulatory functions.
Competency mapping based on the role of the organization and the typical work tasks
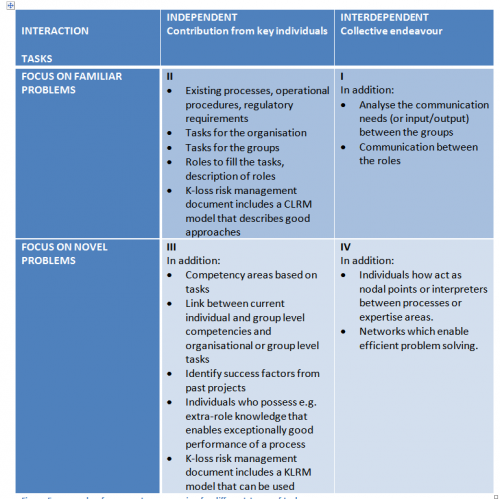
Competency mapping approaches suitable for different work tasks are depicted in Fig 3. If the tasks can be described before-hand and they don’t require much communication (the second quadrant in Fig 3), the existing regulatory requirement, processes and work descriptions are sufficient sources for competency mapping. A hierarchical competency mapping could start from the strategy and business goals of the organization which leads to processes, tasks for groups and roles and finally to competency needs for groups and roles. It is essential for the organization to map which roles are required by which process and what type of individual requirements has to be set for each role. This mapping approach mainly sees organizational competency as a sum of the individual competences and mapping focuses on human capital. This type of mapping approach is described in [3].
If the work tasks are routine, but the communication between the roles is essential (the first quadrant in Fig 3), the competency mapping should, in addition to the existing processes, include also analysing the need for communication between the teams and roles. This can include e.g. input/output requirements of the processes, coordination of work tasks or competencies that are needed for collaboration between roles and teams. This mapping approach focuses on human and formal structural capital.
When the typical tasks of the organization include solving novel problems (the lower row in Fig 3), they cannot be completely pre-described using existing processes and thus the explicitly described processes do not provide a sufficient starting point for mapping of the organizational competency. To maintain and develop competencies in this type of work, constant learning and acquisition of new knowledge is needed. In addition to mapping approaches described in the previous paragraphs, competency mapping that focuses on organizational learning and areas where competencies need to be developed are needed. These mapping approaches start with identifying the expertise areas where novel problems are most likely to occur. After this the current and past success factors and general problem solving approaches are identified. Finally, the organizational learning is addressed.
In organizations where the tasks include novel problems but the roles are mainly independent, (third quadrant in Fig 3) the existing individual competencies can be the basis of some of the organization’s core competencies. In these cases, the organizational competency mapping should also address the human capital imbedded in the individual experts. The mapping should address how the individual competencies are connected to collective competencies and to core competencies and if some individual competencies are critical enablers for upper level competencies.
In organizations where the tasks include novel problems and require collaboration (fourth quadrant in Fig 3), in addition to individual competencies, also the formal and informal networks are an important part of the organizational competencies. The organizational competency mapping should thus address the enablers of effective problem solving in expert networks and learning processes in these networks. The enablers of networking can be, for example, experts how have wide experience that allows them to collaborate over expertise areas and recognise the areas where collaboration is needed.
Competency loss risk assessment
Mapping competency loss risk
Based on the results of competency loss risk assessment, managers should develop a strategic plan addressing organizational competence (knowledge) loss and perform corrective actions Corrective actions mainly can be focused on:
- Determination of prioritized list of competences at risk;
- Critical positions detection;
- Detection of key expert at risk (employees and their critical knowledge and competences);
- Development of substitution plan (reserve) for key employees which are going to leave organization;
- Pairs mentor-successor forming and development of individual plans for knowledge transfer;
- Start of knowledge risk assessment for the critical knowledge identification in accordance with Section 4.
Competences matrix development
As a part of competency loss risk assessment nuclear organizations may create competency matrix in compliance with available HR (staff). The matrix shows demand on competences on the rate of one person covers one competence. Though the practices usually are different, at the same time employee can possess several competences, which are overlapping. This gives nuclear organizations reserve of competences what is very important for successful performance. Managers should take into account all available staff and determine their competences, define which are overlapping. Such approach will provide reflection of current situation, helps to identify competences gaps in specific areas and answered what kind of HR staffing needed for covering them, taking into account new demands. Providing the correction actions on the early stage is proactive response to future risks. It is important to underline that employees can possess knowledge, skills and experience which cover several organizational competences.
References
[1] Bhatt, G.D., Management Strategies for Individual Knowledge and Organizational Knowledge, Journal of Knowledge Management, Vol. 6, Iss. 1., pp. 31-39 (2002).
[2] Blackler, F., Knowledge, Knowledge Work and Organizations: An Overview and Interpretation, Organisation Studies, Vol 16, No. 6, pp. 1021-1046, (1995).
[3] INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Risk Management of Knowledge Loss in Nuclear Industry Organizations, 2006